Fig. 4. Summary figure.
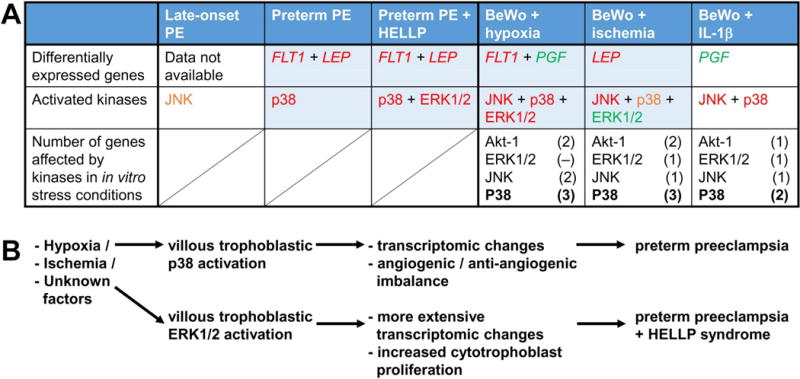
A) The table summarizes differential expression among selected genes and activation among selected kinases in placentas in the disease groups and in BeWo cells in the applied stress conditions. Red letters denote significant increase, orange letters denote marginal increase, while green letters denote significant decrease. Data in boxes highlighted with blue suggest that trophoblastic ischemia and hypoxia may lead to the signaling and transcriptomic changes observed in preterm preeclampsia. Treatments with kinase inhibitors revealed the key role of p38 signaling in impacting trophoblastic gene expression unique to various stress conditions. B) The activation of trophoblastic p38 signaling may be key in placental transcriptomic changes and consequent angiogenic/anti-angiogenic imbalance in preterm preeclampsia. The trophoblastic activation of ERK1/2 signaling may drive the more extensive transcriptomic changes and placental inflammation, and the increased cytotrophoblast proliferation in preterm preeclampsia with HELLP syndrome compared to preterm preeclampsia alone.
