Figure 6. Mechanisms affecting Protein Import.
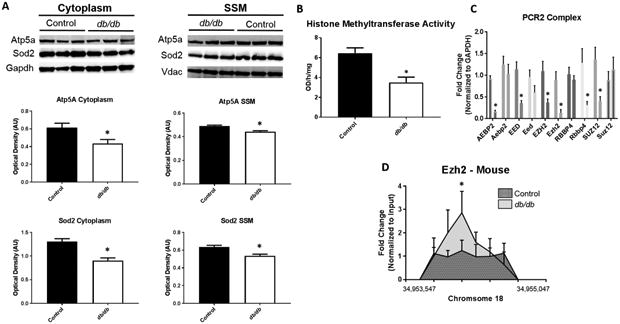
Proteomic analyses revealed changes in the abundance of nuclear-encoded mitochondrial proteins in the mitochondrion following diabetes. (A) Examination of protein import mechanisms for both Atp5a and Sod2 through measurement of cytoplasmic and SSM protein content in control (n = 7) and db/db (n = 5) mouse whole heart. To begin to understand epigenetic consequences (B) global histone methyltransferase activity for H3K27me3 was assessed in control (n = 5) and db/db (n = 5) mouse whole heart. Further, (C) constituents of the PCR2 complex were measured through qPCR in both human (ND and T2DM, n = 5) and mouse (control and db/db, n = 5) cardiac tissue. At the Hspa9 promoter loci, (D) ChIP pulldown and qPCR was performed for Ezh2. Values are expressed as means ± SEM. *P ≤ 0.05 for control vs. diabetes mellitus. ChIP-qPCR samples were normalized to their respective input control. GAPDH was used to normalize PCR2 components. H3K27me3 = histone 3 lysine 27 tri-methylation, PCR2 = Polycomb Repressive Complex 2, HSPA9 = Heat Shock Protein Family A (Hsp70) Member 9, AEBP2 = AE Binding Protein 2, EED = Embryonic Ectoderm Development, EZH2 = Enhancer of zeste homolog 2, RBBP4 = RB Binding Protein 4, SUZ12 = Suppressor of Zeste 12 Homolog T2DM = type 2 diabetes mellitus.
