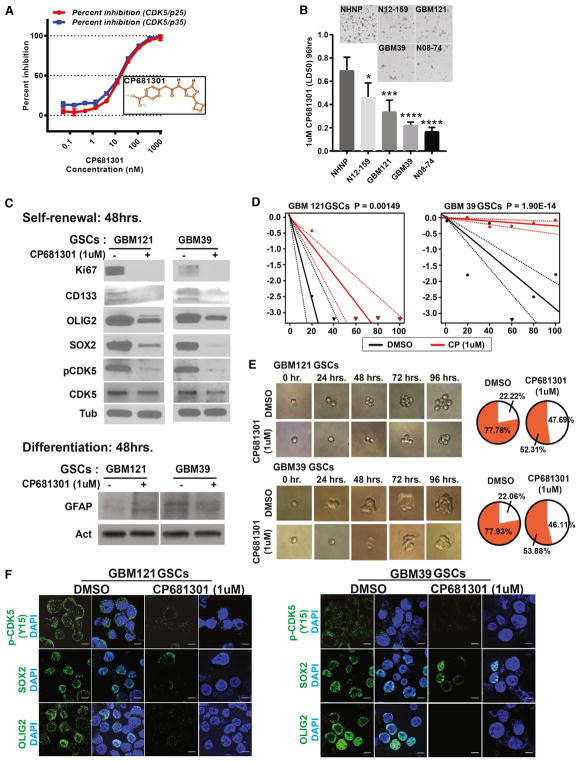
Figure 3. CDK5 Regulates Self-Renewal Properties in GSCs.
(A) To determine if CDK5 regulates self-renewal of GSCs, first we tested the potency of a highly specific CDK5 inhibitor called CP681301 from Pfizer. Using active CDK5-p35 and CDK5-p25 as enzymes, we established a dose-response curve for CP681301 in order to find the doses that successfully inhibit kinase catalytic activity of both protein complexes in vitro. 1 μM CP681301 was the optimal concentration that suppressed 100% of CDK5-p35 and CDK5-p25 catalytic activity.
(B) CP681301 (1 μM) for 96 hr is significantly less toxic to NHNPs (control) than GSCs. *, <0.05, ***, <0.001, ****, <0.0001.
(C) CP681301 treatment for 48 hr suppressed active CDK5 and reduced stem cell markers CD133, OLIG2, and SOX2 and cell proliferation marker KI67 in GSCs but did not change differentiation markers (GFAP).
(D and E) Using a limiting dilution assay (D) and visual demonstration (E), we established that CP681301 also reduces the self-renewal properties of GSCs.
(F) Immunocytochemistry showed that GSCs from two neurosphere lines have reduced levels of active CDK5 and stem cell markers SOX2 and OLIG2 (Figure S6).