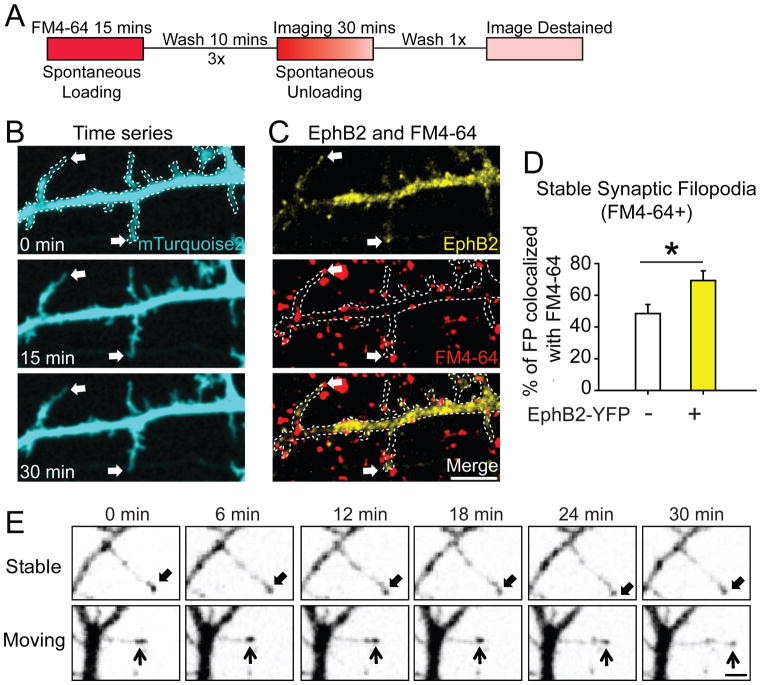
Figure 2. EphB receptors cluster at the tip of moving and stable filopodia, and colocalize with synaptic release sites.
(A) Experimental procedure for labeling of presynaptic release sites as in ((Wilhelm et al., 2010), See Methods for details). (B) Representative images show filopodia stable for 30 minutes in neurons transfected with mT2 (Arrows). (C) The same dendrite as in B overlaid with images of EphB2-YFP (yellow) and synaptic release sites (red, labeled with FM4-64). Arrows indicate EphB2-YFP+ filopodial tips colocalized with FM4-64. Dashed lines show the morphology of transfected neurons. Scale bar = 5 μm. (D) Quantification of colocalization (EphB2+: 69 ± 6%, n = 9; EphB2-: 49 ± 6%, n = 9, p = 0.024, t-test). * p < 0.05. Error bars indicate SEM (E) Representative images from 30-minute time-lapse movies of DIV7-10 neurons transfected with EphB2-YFP. Two types of filopodia were identified (Stable and Moving filopodia). Arrows indicate EphB2+ tips across time window. Scale bar = 2 μm. See also Movie S1.