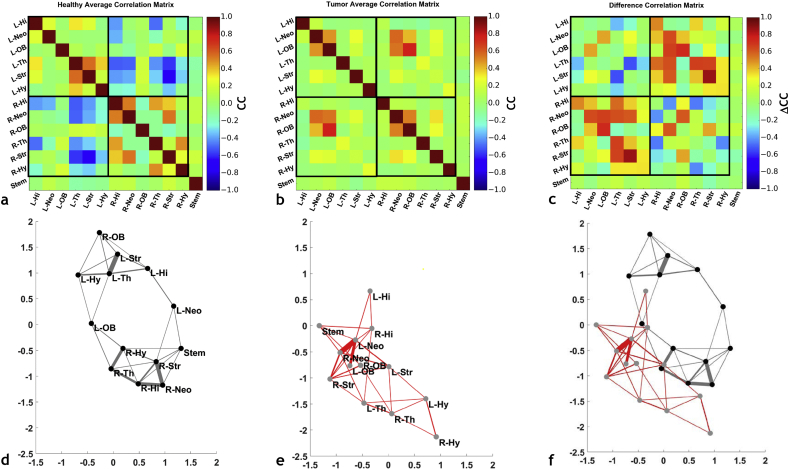
Fig. 2.
Brain tumors disrupt inter- and intra-hemispheric resting-state functional connectivity. Correlation coefficient (CC) matrices illustrating the average resting-state functional connectivity for: (a) ROI from healthy mice; (b) ROI from tumor-bearing mice. (c) The ‘difference’ matrix between tumor-bearing and normal mouse ROI illustrating the inter-ROI connectivity most affected by the presence of a tumor. (d-e) Kamada-Kawai (KK) plots corresponding to the CC matrices in (a) and (b). (d) Average KK plot for normal mouse brains, (e) average KK plot for tumor-bearing mouse brains, and (f) an illustration of the alterations in connectivity between tumor-bearing and normal brains by overlaying the KK-plots in (d) and (e). Labels have been omitted in (f) for clarity. For each KK-plot, the edge thickness represents the strength of the connectivity between the nodes (i.e. ROI).