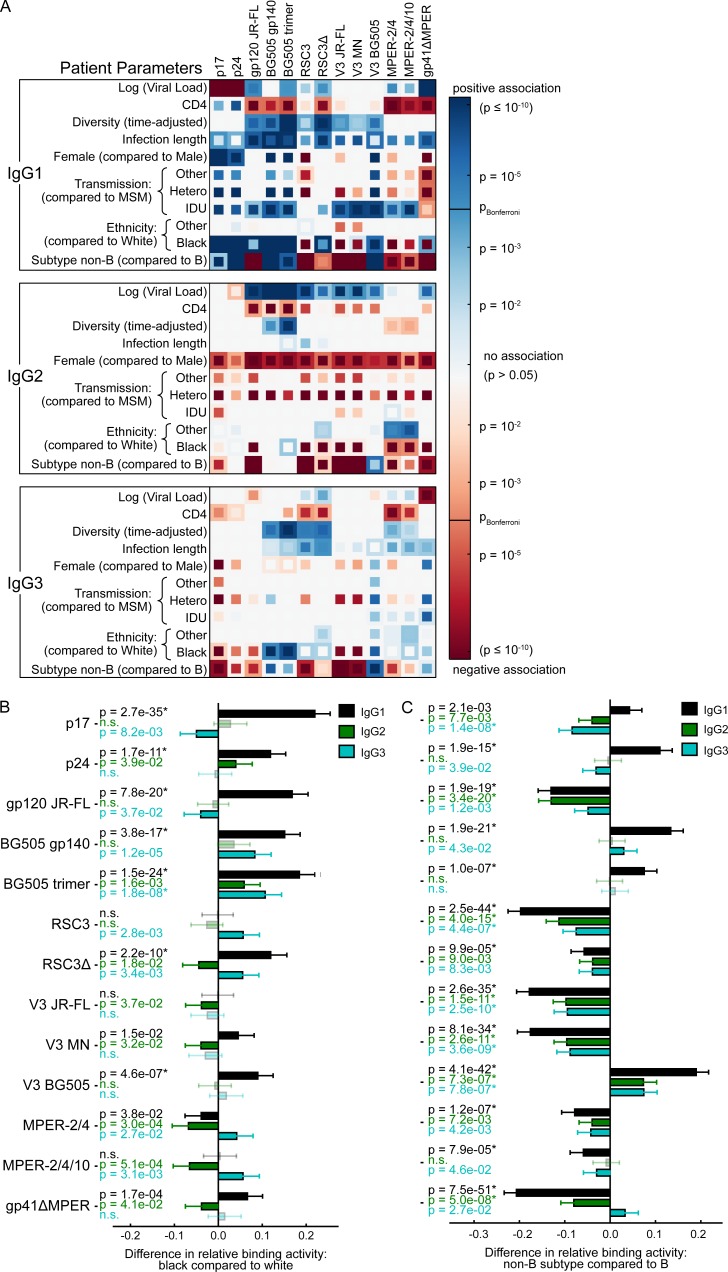
Figure 2.
Influence of host, viral and disease parameters on binding antibody responses across all ethnicities. (A) The influence of the virus load, CD4 count, viral diversity, length of untreated HIV-1 infection, transmission route, gender, ethnicity, and HIV-1 subtype on binding antibody responses to each tested HIV-1 antigen was determined by univariable (inner squares) and multivariable (outer squares) linear regression for all three IgG subclasses (n = 3,159). Only significant associations (P < 0.05) are colored, and the Bonferroni-corrected significance threshold (P = 0.00012) is shown in the color map. Color intensity represents the significance level of positive (blue) and negative (red) associations. See Table S3 for detailed regression results. (B and C) Impact of the indicated parameter on the relative IgG1 (black), IgG2 (green), and IgG3 (blue) binding activity, based on the same multivariable linear regression analysis as in A. Error bars depict the 95% confidence intervals. Nonsignificant associations are marked by n.s. and are shown in lighter color shades. * highlights significant associations when using a Bonferroni correction for multiple testing. (B) Influence of black compared with white individuals. (C) Non–B-infected compared with B-infected individuals.