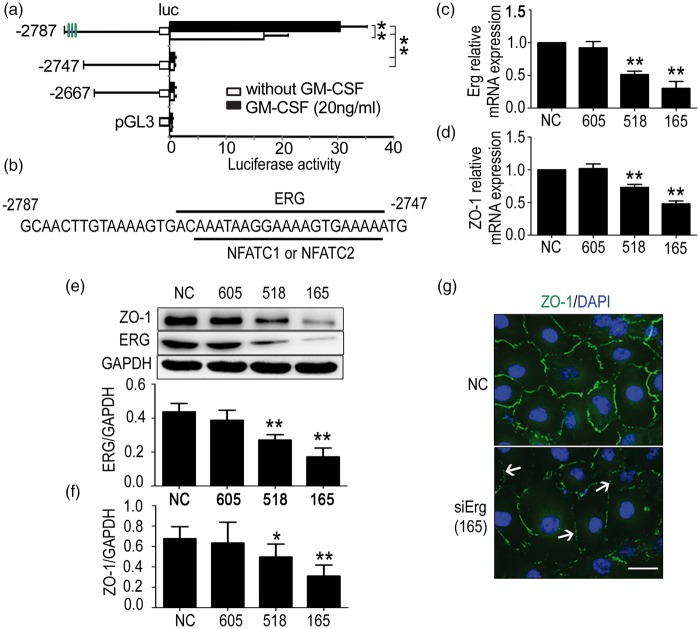
Figure 2.
The erythroblast transformation-specific (ETS) transcription factor ERG regulates zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) transcription in human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs). (a) Results of dual luciferase reporter experiments. Different pGL3 vectors cloned with different truncations of the ZO-1 promoter were cotransfected with pRL-TK into HBMECs stimulated with or without GM-CSF. After 24 h, luciferase activity was detected. One-way ANOVA was used to compare luciferase activity. Data are shown as the mean ± SD, n = 3. **p < 0.01 vs. the luciferase activity of the − 2787 truncation. (b) Paradigm of possible transcription factors. ERG, NFATC1 and NFATC2 transcription factors, which bind to the −2787 to −2747 truncation, were predicted using the Matinspector online software. (c) Effect of ERG interference on ZO-1 expression. SiErg-518 and siErg-165 reduced ERG and (d) ZO-1 mRNA levels significantly. (e) SiErg-518 and siErg-165 decreased ERG and (f) ZO-1 protein levels significantly. One-way ANOVA was used for repeated measurements. Data are shown as the mean ± SD, n = 3.*p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 vs. NC. (g) Immunofluorescent staining of ZO-1 expression. HBMECs from the NC and siErg-165 groups were stained with ZO-1 (green) and 4,6-diamidino-2-phenyl-indole (DAPI) (blue), and the down-regulation and disassembly of ZO-1 (not continuous) were indicated by the white arrows. Scale bar = 20 µm.