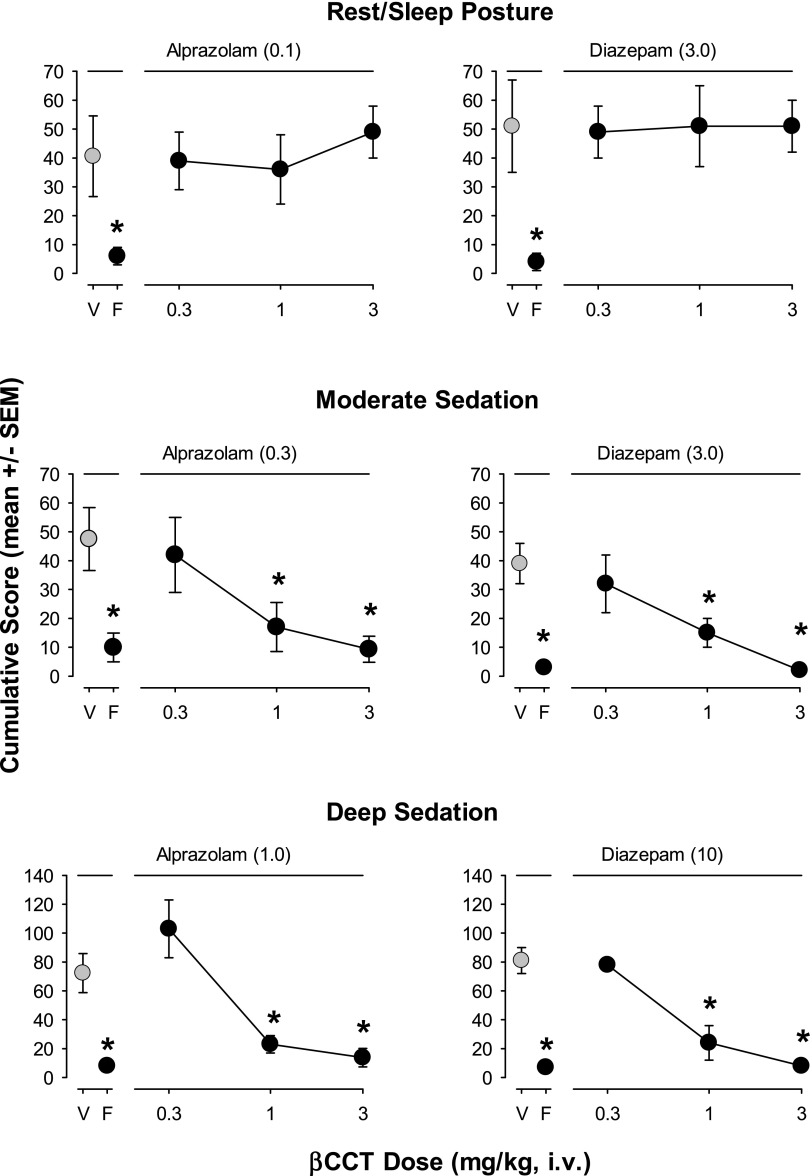
Fig. 5.
Differential effects of pretreatment with βCCT (α1GABAA-preferring antagonist) and flumazenil (nonselective benzodiazepine-site antagonist) on drug-induced sedative behaviors. Data are mean ± S.E.M. of scores cumulated across a test day with multiple observation periods. Multiple doses of βCCT (0.3–3.0 mg/kg, i.v.) and a single dose of flumazenil (“F,” 0.3 mg/kg, i.v.) were administered prior to the session in which peak doses of alprazolam or diazepam were administered (benzodiazepine dose depended on individual dose-response function for each behavioral effect). Top panels: Rest/sleep posture induced by alprazolam (0.1 mg/kg, data point above V, vehicle) or diazepam (3.0 mg/kg, i.v.) was attenuated by flumazenil (F) but not βCCT; middle panels: Moderate sedation was induced by alprazolam (0.3 mg/kg, i.v.) or diazepam (3.0 mg/kg, i.v.) and blocked by both flumazenil (0.3 mg/kg, i.v.) and dose-dependently by βCCT (1.0 and 3.0 mg/kg, i.v.); bottom panels: Deep sedation was induced by the highest doses of alprazolam (1.0 mg/kg) or diazepam (10 mg/kg) and attenuated by flumazenil (0.3 mg/kg) and dose-dependently by βCCT (1.0 and 3.0 mg/kg). Note that *P ≤ 0.05, vs. vehicle (V), Bonferroni t tests, n = 4.