Fig. 1.
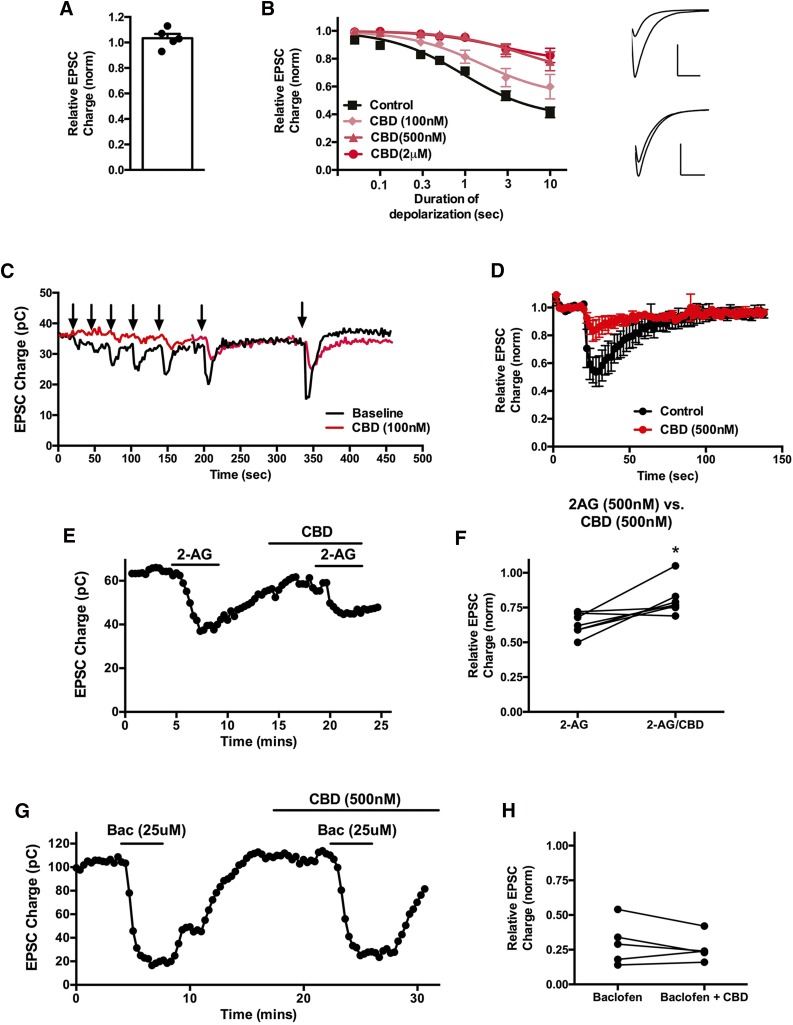
CBD suppresses CB1 receptor–mediated DSE. (A) CBD (500 nM) does not directly inhibit excitatory postsynaptic currents. (B) The 100 or 500 nM CBD treatment (5 minutes) shifts the response curve for DSE in a concentration-dependent manner. Inset shows sample EPSCs before and after DSE under baseline conditions (top) and after CBD (500 nM) treatment (bottom). (C) Sample time course showing DSE responses to progressively longer depolarizations before and after 100 nM CBD treatment. (D) Averaged DSE time course in response to 3-second depolarization before and after 500 nM CBD treatment. (E) Representative experiment showing that half-maximal 2-AG responses (500 nM) are diminished by 500 nM CBD. (F) Inhibition by 2-AG (500 nM) alone gives a stronger response than in the presence of CBD (500 nM). (G) Representative experiment showing that GABA-B responses (25 μM baclofen) are unaltered by 500 nM CBD treatment. (H) Inhibition of EPSCs by baclofen alone or in combination with CBD (500 nM). *P < 0.05 by paired t test.