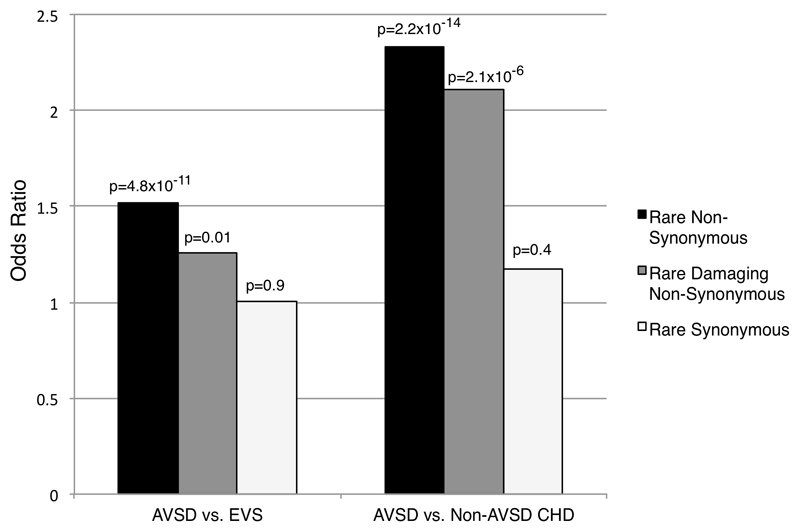
Figure 1. Mutation burden analysis across 112 genes with biological relevance to AVSD.
All rare, non-synonymous variants in the gene were collapsed for each individual to allow a patient level analysis. Odds ratio (OR) for the number of individuals with rare non-synonymous (blue), rare/damaging non-synonymous (red) and synonymous (green) variants across 112 genes in the AVSD cohort compared to EVS controls and non-AVSD CHD cohort with p values are shown. The AVSD cohort showed enrichment of rare non-synonymous variants (OR 1.5, p = 4.7 x 10-11) and rare damaging non-synonymous variants (OR 1.3, p = 0.01) compared to EVS cohort. The AVSD cohort showed a similar enrichment of rare non-synonymous variants (OR 2.3, p = 2.2 x 10-14) and rare damaging non-synonymous variants (OR 2.1, p = 2.1x10-6) compared to the non-AVSD CHD cohort. There was no difference between the cohorts in rare synonymous variants (AVSD vs. EVS, OR 1.0, p = 0.9; and AVSD vs. non-AVSD CHD, OR = 1.2 p = 0.2).