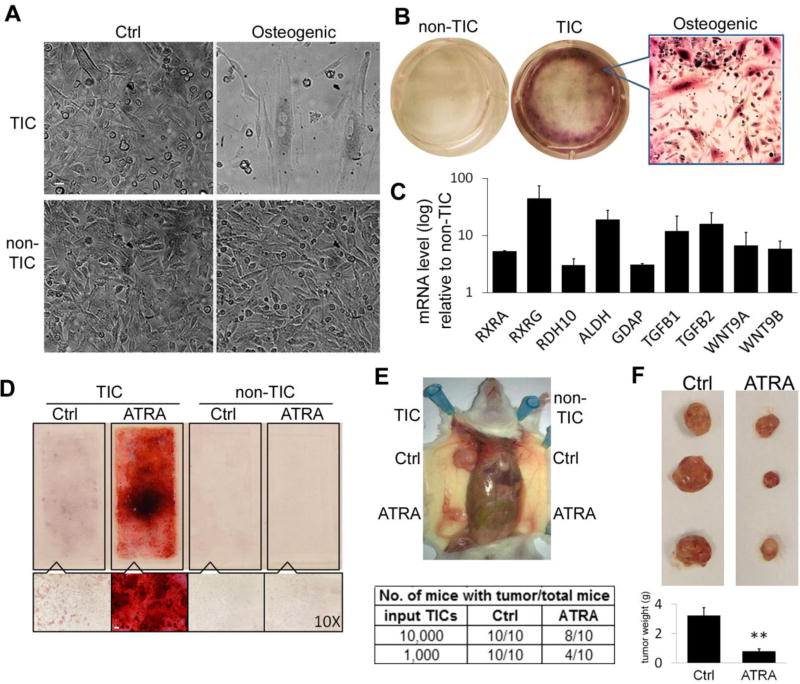
Figure 4. TICs Undergo Osteogenic Diffe rentiation by ATRA Treatment with Decreased Malignancy.
(A) Under osteogenic differentiation conditions, morphological alterations were observed in TICs in 10 days. (B) Osteogenic differentiated HLA-I(−) TICs showed strong positive Alizarin-Red-S staining. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR results showed highly expressed RAR pathways genes in HLA-I(−) TICs compared to non-TICs. Data represent the mean ± SD. (D) ATRA treatment induced osteogenic differentiation of TICs in vitro. Top: 4-well chamber slide stained with Alizarin-red-S; Bottom: bright field microscope (10×). Scale bar: (A,B):10 µm; (D):100 µm (E) TICs and non-TICs were treated in vitro with ATRA before transplanted into NGS mice. Tumor formation by ATRA treated TICs were significantly decreased. (F) Mice transplanted with TICs cells were treated orally with ATRA or DMSO every other day for 6 weeks. ATRA treatment inhibited the tumor formation by TICs in vivo. Top: Representative tumors formed by HLA-I(−) cells; Bottom: average tumor mass (error bars represent the standard errors, **: P<0.01).