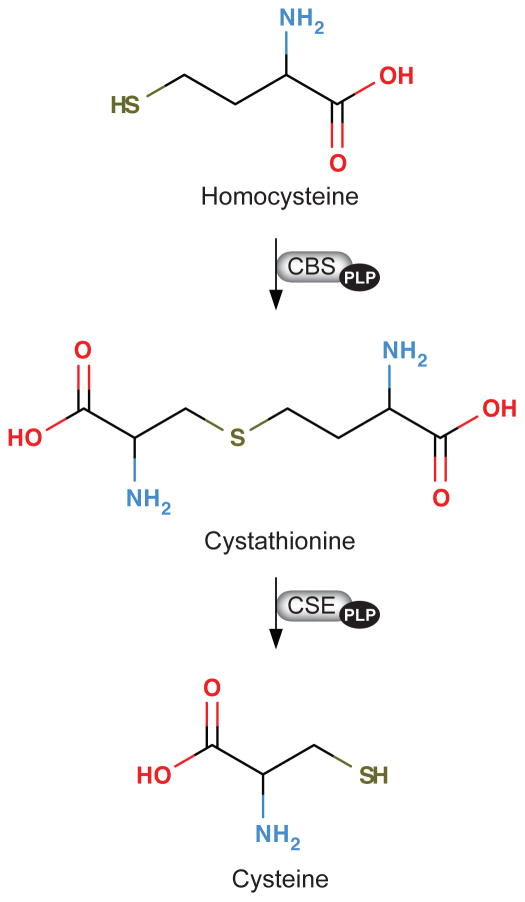
Figure 3.
The transsulfuration pathway. Homocysteine is form by hydrolysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine, which is formed from S-adenosylmethionine during transmethylation reactions (not shown). Homocysteine is either remethylated to methionine (not shown) or converted to cysteine via the transsulfuration pathway, where homocysteine is converted to cysteine through the sequential action of two vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5′-phosphate)-dependent enzymes, cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS; EC 4.2.1.22) and cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE; EC 4.4.1.1).