Figure 1. Restriction of atrial and ventricular identity.
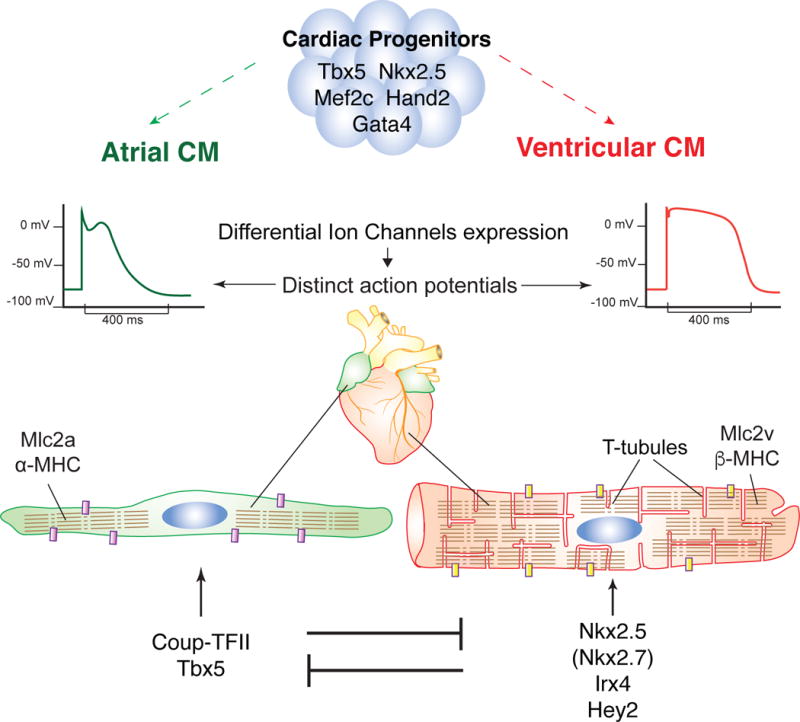
(A) Atrial (green) and ventricular (red) cells arise from distinct yet overlaping sets of cardiac progenitors, characterized by the expression of transcription factors such as Tbx5, Nkx2.5, Mef2c, Hand2 and Gata4. (B) Atrial and ventricular myocytes display distinct physiological, structural and molecular differences. For example, ventricular cardiomyocytes display a flatter action potential plateau, have specialized T-tubule structures and express different gene variants e.g. Mlc2v/Mlc2a, β-MHC/α-MHC. (C) Atrial and ventricular myocytes each express a mutually exclusively transcriptional program that continues to promote their own identity and suppresses the other.
CM: Cardiomyocyte, Purple/Yellow block: different ion channels, Segmented lines represent sacromeres.
