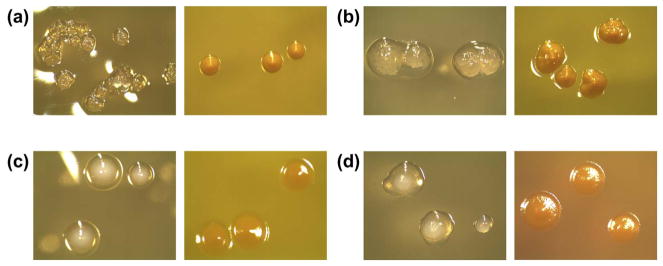
Fig. 1.
Typical colony morphology combinations seen on MS ID plates (left images: SB20M, right images: SMAB): (a) S. mutans, (b) S. mutans, (c) S. sobrinus, (d) S. sobrinus. On SB20M, S. mutans forms clear, rough colonies that may be surrounded by a drop of clear polysaccharide. S. sobrinus forms opaque white colonies surrounded by or appearing to sit on top of clear polysaccharide. On SMAB, both species form yellow colonies with S. mutans colonies being slightly mounded and S. sobrinus colonies appearing flat. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)