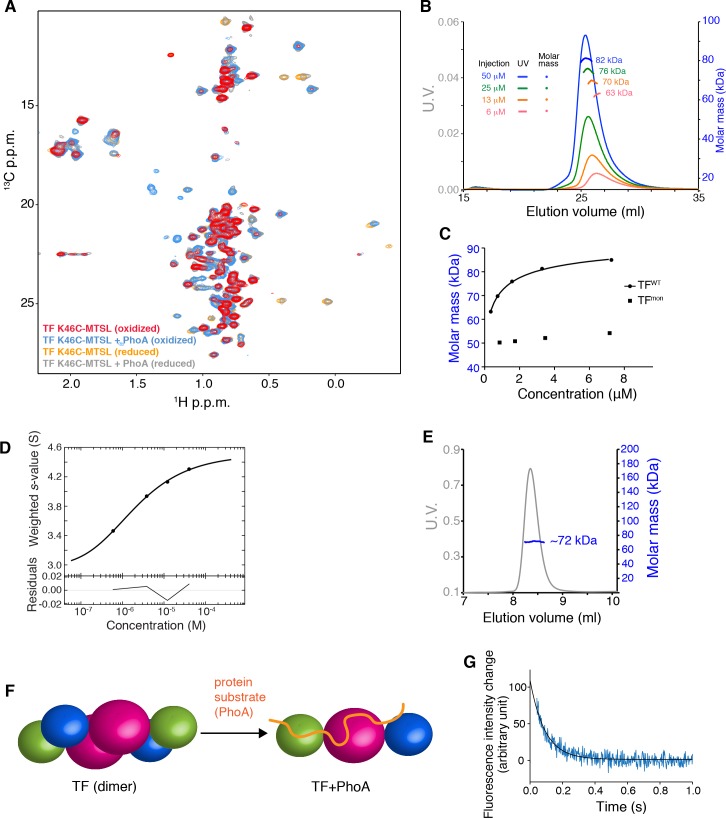
(A) Observation of PRE for TF K46C attached with MTSL in the presence and absence of its substrate PhoA. Overlay of 1H-13C methyl HMQC spectra of [U-2H; Met-13CH3; Ile-δ1-13CH3; Leu,Val-13CH3/13CH3]-labeled TF K46C attached with MTSL in oxidized (paramagnetic) and reduced (diamagnetic) conditions. Reduced spectra were acquired in the presence of ascorbic acid. A number of resonances of unliganded TF broadened out in paramagnetic spectrum indicate strong intermolecular PRE due to dimer formation. Addition of unfolded substrate protein PhoA retrieved the broadened resonances, indicating the dissociation of the dimer by the interaction with the substrate. (B) SEC-MALS of TF injected at varying concentrations. Injection at lower concentration resulted lower molecular mass, indicating increase of monomer fraction at lower concentration. (C) Plots of molar mass as a function of concentration. The molar mass was estimated by SEC-MALS for TF and TFmon (TF V39E/I76E/I80A) injected at varying concentrations. The solid line represents the fit of the data to a model of monomer-dimer equilibrium. (D) Sedimentation velocity-AUC isotherm of TF. Best-fit isotherms of the weight-average s-values, sw(c), obtained by integration of c(s) distributions of TF over the entire s-range for each loading concentration in a dilution series. The solid line is the fitted isotherm to a reversible monomer-dimer self-association model. The dissociation constant Kd is 1.687 [1.482, 1.914] µM. Errors of the constants represent the 68.3% confidence interval (CI) using an automated surface projection method. (E) SEC-MALS of TF in complex with PhoA1-141 shows that TF binds to PhoA as a monomer (TF-PhoA theoretical molar mass: 66 kDa). (F) Schematic showing the monomerization of TF upon substrate-binding. (G) Dissociation kinetics of the TF dimer. Dissociation of the dimer was initiated by 10-fold dilution of TF to final concentration of 0.1 μM at 22°C. Solid line represents the fit of the data to a single exponential function yielding the dissociation rate (kdiss) of ~ 10 s−1.