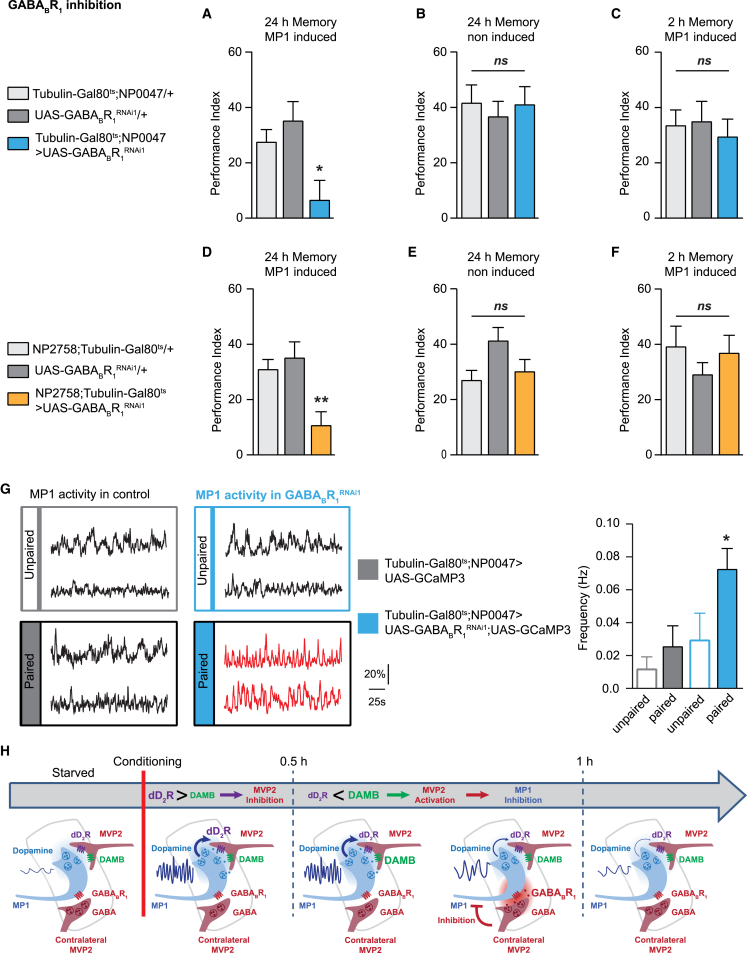
Figure 4.
D-GABABR1 Downregulation in MP1 Impairs Appetitive LTM and Induces Persistent MP1 Oscillations after Training
(A and B) In (A), knockdown of D-GABABR1 in MP1 adult neurons impaired LTM (n = 9), F(2, 27) = 5.41, p < 0.05; whereas in (B), the non-induced controls displayed normal LTM (n = 10), F(2, 29) = 0.19, p = 0.83.
(C) Expression of D-GABABR1 RNAi in MP1 adult neurons did not impair 2-hr memory (n = 12), F(2, 33) = 0.19, p = 0.83. Similar results were observed using a second non-overlapping D-GABABR1 RNAi (see Figure S4).
(D and E) In (D), LTM was also impaired when a second MP1 inducible driver (NP2758;Tubulin-Gal80ts) was used to downregulate D-GABABR1 at the adult stage (n = 12), F(2, 33) = 6.94, p < 0.05; whereas in (E), LTM was normal in non-induced controls (n = 12), F(2, 33) = 2.93, p = 0.07.
(F) Inhibition of D-GABABR1 using this second MP1 inducible driver did not affect 2-hr memory (n = 11), F(2, 30) = 0.71, p = 0.50. See Table S2 for sugar perception and olfactory acuity controls.
(G) The frequency of MP1 calcium oscillations was significantly higher 1.5 hr after appetitive training in flies co-expressing D-GABABR1 RNAi and GCamP3 in adult MP1 neurons than in unpaired controls and both paired and unpaired flies that do not express the D-GABABR1 RNAi (n = 9), F(3, 32) = 4.25, p < 0.05. Illustrative examples of MP1 neuron recordings are displayed for each genotype and condition; controls are indicated in black, and the condition in which paired trained flies express D-GABABR1 RNAi in MP1 neurons is indicated in red. Similarly to the oscillations frequency, the quality factor of MP1 calcium oscillation was increased, whereas the amplitude of MP1 calcium oscillations was not affected (see Figures S4D and S4E). Control imaging experiments using the other odorant used for behavior experiment (methylcyclohexanol) were done to assess that the effect of inhibiting metabotropic GABA signalization in MP1 is not odorant specific (see Figures S4I–S4M).
(H) Schematic depicting how the MP1 and MVP2 neurons regulate their activity over LTM formation. The different metabotropic receptors involved in this feedback loop are represented, and the peduncle area is represented by the light gray outlines.
Error bars indicate mean ± SEM. Statistical tests were performed using one-way ANOVA. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, in post hoc comparison; ns, not significant.