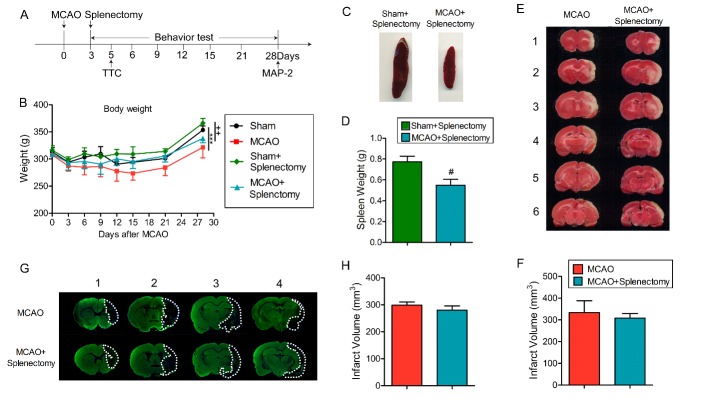
Figure 1.
Delayed splenectomy after ischemic stroke shows no effect on acute and long-term brain tissue loss. Rats were subjected to 90 min MCAO followed by delayed splenectomy at 3 days after ischemic stroke. (A) Illustration of the experimental timelines. (B) Body weight was examined up to 28 days after MCAO. n=6 rats for sham groups; n=9 rats for MCAO groups. ***p<0.001: Sham vs MCAO; +++p<0.001: Sham+Splenectomy vs MCAO+Splenectomy; ##p<0.01: MCAO vs MCAO+Splenectomy group by one-way ANOVA repeated measurement. (C) Representative images of spleen from sham+splenectomy and MCAO+splenectomy groups at 3 days after MCAO. (D) Quantification of spleen weight at 3 days after stroke. n=9 for each group. #p<0.05 by Student’s t-test. (E) Representative images of TTC-stained coronal brain sections from MCAO and MCAO + splenectomy groups at 5 days after MCAO. (F) Quantification of infract volume 5 days after MCAO. n=5-6 for each group. #p<0.05 by Student’s t-test. (G) Representative images of MAP-2 staining in MCAO and MCAO + splenectomy groups at 28 days after MCAO. (H) Quantification of brain tissue loss at 28 days after MCAO. n=5-6 for each group. Values are mean ± SEM.