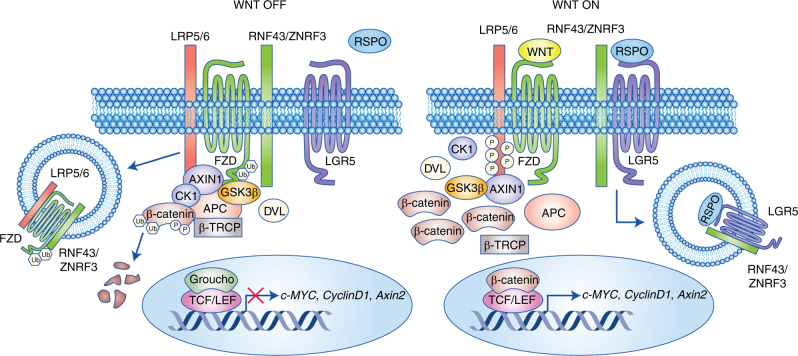
Fig. 1. LGR5 promotes Wnt/β-catenin signalling.
LGR5 has a well-defined function in the promotion of Wnt/β-catenin signalling in normal intestinal stem cells. Without RSPO bound to LGR5, Wnt signalling is kept low through the action of transmembrane E3 ligases RNF43/ZNRF3, which internalise and degrade the Wnt receptors Frizzled and LRP5/6. This leads to downstream β-catenin degradation and subsequent repression of Wnt target genes. The binding of RSPO to LGR5 sustains Wnt signalling by neutralising the RNF43/ZNF3 ligases, which can no longer remove Wnt receptors from the cell membrane. FZD and LRP5/6 are free to bind Wnt ligands leading to stabilised β-catenin and downstream activation of Wnt target genes such as c-MYC, CyclinD1 and Axin2