Figure 1.
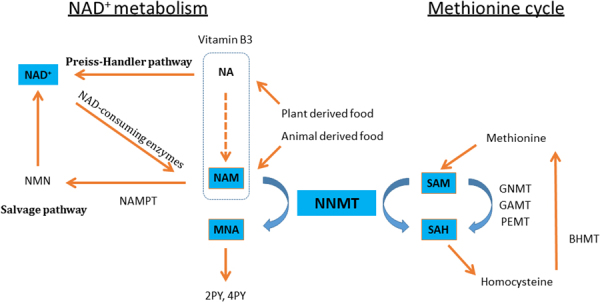
NNMT links NAD+ and methionine metabolism. NA is metabolized to NAM via the amidation pathway. NA and NAM are the common forms of Vitamin B3, and are converted to NAD+ through the Preiss-Handler and salvage pathways, respectively. NAD+ is metabolized to NAM by the enzymatic activities of NAD+-consuming enzymes (Sirtuins, PARPs, cADPR synthases). NNMT methylates NAM, using SAM as a methyl donor, yielding MNA and SAH. MNA and its oxidation products, 2PY and 4PY are major metabolites of NAM. GNMT, GAMT and PEMT are the main methyltransferases mediating SAM catabolism in the liver. BHMT1 is the enzyme for the re-methylation of homocysteine to generate methionine. Abbreviations: NA, nicotinic acid; NAM, nicotinamide; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NMN, nicotinamide mononucleotide; PARP, poly adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase; cADPR, cyclic adenosine diphosphate-ribose; NAMPT, nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase; NNMT, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase; MNA, 1-methylnicotinamide; 2PY, N-methyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide; 4PY, N-methyl-4-pyridone-5-carboxamide; SAM, S-adenosylmethionine; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; GNMT, glycine N-methyltransferase; GAMT, guanidinoacetate N-methyltransferase; PEMT, phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase; BHMT, betaine homocysteine methyltransferase.
