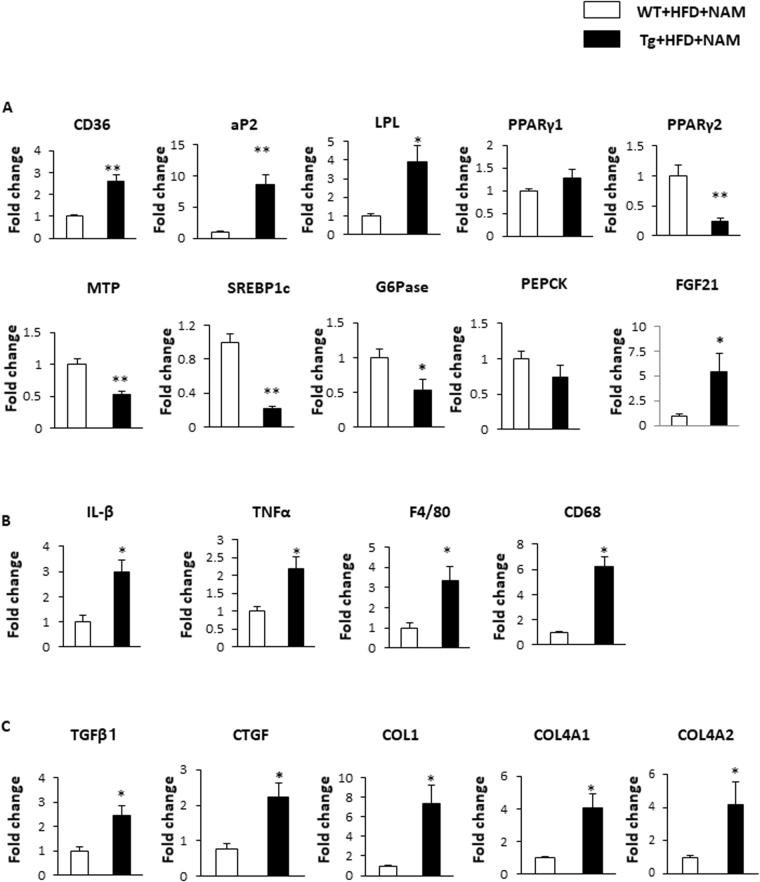
Figure 5.
NNMT overexpression induces genes involved in FFA uptake, VLDL secretion, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver. Total RNA samples, isolated from the livers of NMMT Tg mice (black bars) and WT littermates (white bars) on an HFD with NAM for 7 months, were analysed using real-time RT-PCR. The amounts of each mRNA related to hepatic lipid metabolism (A), tissue inflammatory responses (B), and tissue fibrosis (C) were measured and normalised to β-actin mRNA levels. The values shown are the means ± SEM (n = 3–6 per group). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus WT mice. Abbreviations: NAM, nicotinamide; NNMT, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase; HFD, high fat diet; Tg, transgenic; WT, wild type; FFA, free fatty acid; VLDL, very low density lipoprotein; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; PPAR, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; MTP, microsomal triglyceride-transfer protein; SREBP1c, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c; G6Pase, glucose-6 phosphatase; PEPCK, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; IL, interleukin; TNF-α, tissue necrosis factor-α; TGFβ1, transforming growth factor β1; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; COL, collagen.