Fig. 1.
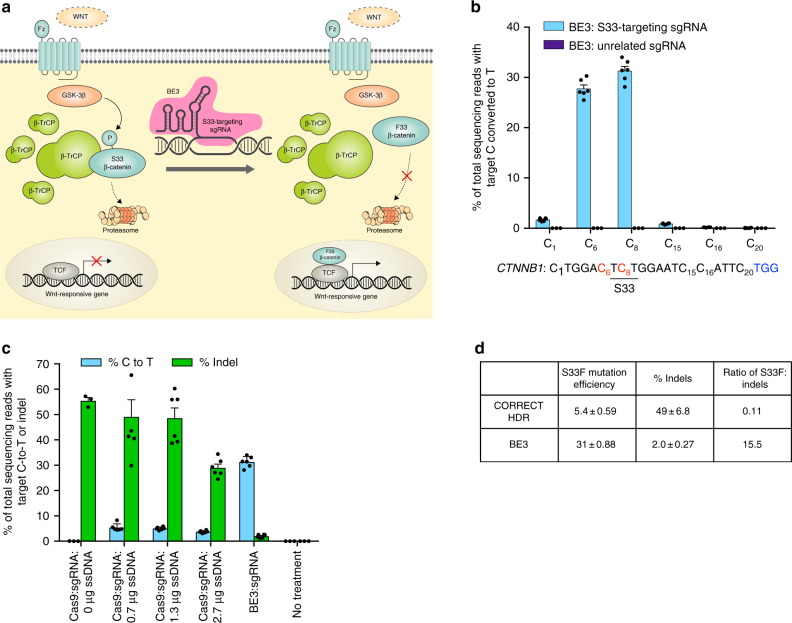
Base editing strategy and comparison of HDR and base editing following plasmid delivery. a Schematic representation of the canonical Wnt pathway and a base editing strategy to stabilize β-catenin. In the absence of Wnt signaling, β-catenin is phosphorylated at Ser 33 by GSK-3β and degraded in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. Base editing with BE3 precisely mutates the Ser 33 codon to instead encode Phe, which cannot be phosphorylated. The resulting S33F β-catenin has an extended half-life and can activate target gene transcription by binding with TCF/LEF transcription factors. b HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing BE3 and S33-targeting sgRNA, or BE3 and an unrelated sgRNA. The percentage of total sequencing reads (with no enrichment for transfected cells) with C8 converted to T8 (resulting in the S33F mutation) was measured with high-throughput sequencing (HTS). c Plasmid delivery of Cas9 and BE3 (750 ng) with S33-targeting sgRNA (250 ng) into HEK293T cells using 1.5 µL of Lipofectamine 2000 per well of a 48-well plate. C-to-T conversion efficiency and d product selectivity ratio (desired S33F mutation: undesired indel ratio) resulting from the best-performing ratio of Cas9:sgRNA:ssDNA template and BE3. Values and error bars reflect mean ± S.E.M. of three biological replicates performed on separate days