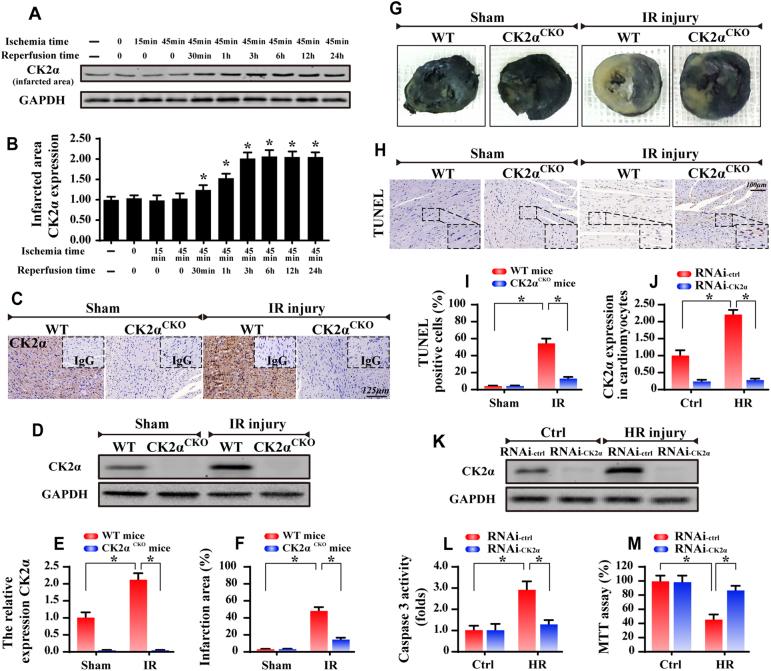
Fig. 1.
Upregulation of CK2α at the infarcted area. WT mice and CK2αCKO mice underwent the 45-min ischemia and 0–24-hour reperfusion (IR injury, n = 6/group). In vitro, 45-min of hypoxia and 6-hour of reoxygenation (HR) was used to mimic the IR injury. Meanwhile, the loss-of-function assay about CK2α was conducted via siRNA (RNAi-CK2α) or control siRNA (RNAi-ctrl) in cardiomyocytes. a CK2α expression in the infarcted area. b Quantitative analysis of the relative expression of CK2α. C. The immunohistochemistry of CK2α in heart. d, e The western blots were used to confirm the CK2α expression in WT mice or CK2αCKO mice under IR injury. f, g Representative images of heart sections with TTC and Evans Blue staining of the infarcted area. Bar graph indicates the infarct size. h, i TUNEL assay for cellular apoptosis analysis. j, k The control siRNA (RNAi-ctrl) and CK2α-siRNA (RNAi-CK2α) were transfected into cardiomyocytes. The transfection efficiency was confirmed by western blots. l, m Caspase3 activity and MTT assay were used to detect the cellular viability and apoptosis. The data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05