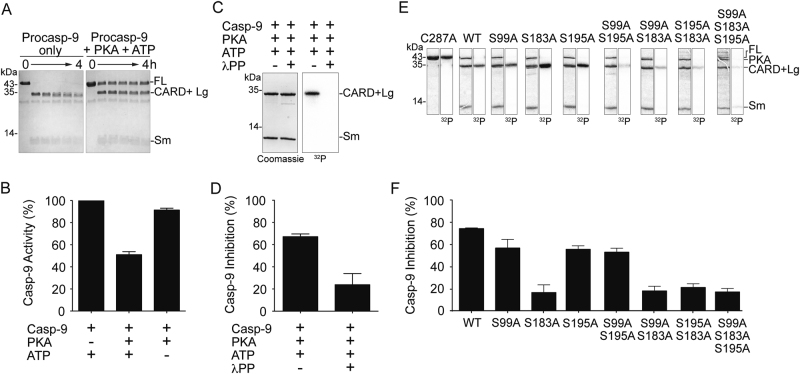
Fig. 2.
Phosphorylation of casp-9 by PKA results in significant inhibition of casp-9. a Active PKA inhibits self-processing of procasp-9. Full-length (FL) WT procasp-9 rapidly undergoes self-cleavage to generate the CARD + Large (Lg) and Small (Sm) subunits as assessed by Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE analysis. Addition of PKA and ATP to procasp-9 slows the rate of self-cleavage, so that casp-9 remains predominantly in the full-length, uncleaved form even after 4 h incubation. b Addition of active PKA to cleaved casp-9 WT results in a two-fold decrease in caspase activity after 2 h as measured by the hydrolysis of the fluorogenic casp-9 substrate Ac-LEHD-afc, suggesting that PKA treatment leads to inhibition. Percent casp-9 activity is normalized against activity in the absence of PKA. c Casp-9 is phosphorylated by PKA only in the CARD + Lg region, as detected by autoradiography after in vitro phosphorylation using [γ-32P] ATP for 4 h. There is no visible phosphorylation in the Sm subunit. PKA is phosphorylated during overexpression in bacteria [66], so it does not get efficiently labeled by [γ-32P] ATP. Treatment of PKA-phosphorylated casp-9 with λ protein phosphatase (λPP) results in dephosphorylation as manifested by loss of signal in the autoradiogram (labeled here and in the succeeding figures as 32P). d Phosphorylation of casp-9 is reversible. Casp-9 phosphorylated by PKA is inhibited. Treatment of phosphorylated casp-9 with λ protein phosphatase (λPP) relieves the inhibition. Percent inhibition for phosphorylated casp-9 (with both PKA and ATP present) was normalized against activity in the non-phosphorylated form (with PKA but no ATP present). e Unphosphorylatable alanine variants (single, double and triple alanine substitutions at phosphorylated serines) and catalytic site-inactivated variant C287A were subjected to in vitro phosphorylation by PKA for 4 h. Double alanine variants show (observed by Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE analysis in the first of each pair of panels) decreased levels of phosphorylation as the weaker intensity of the bands in the autoradiogram (second of each pair of panels and Table S1). The triple alanine variant shows only weak, non-specific phosphorylation in the small subunit, indicating that all three sites S99, S183, and S195 are phosphorylated by PKA. f Inhibition by phosphorylation of casp-9 WT and alanine variants. Only when S183 is available to be phosphorylated (WT, S99A, S195A, and S99A/A195A) does casp-9 experience significant inhibition. All S183A variants are insensitive to PKA-mediated inhibition. The catalytic parameters of alanine variants are indicated in Table 1. Percent inhibition for phosphorylated casp-9 was determined as in d. For b, d and f, data shown are means (± SEM) of three independent trials done on three separate days.