Figure 4.
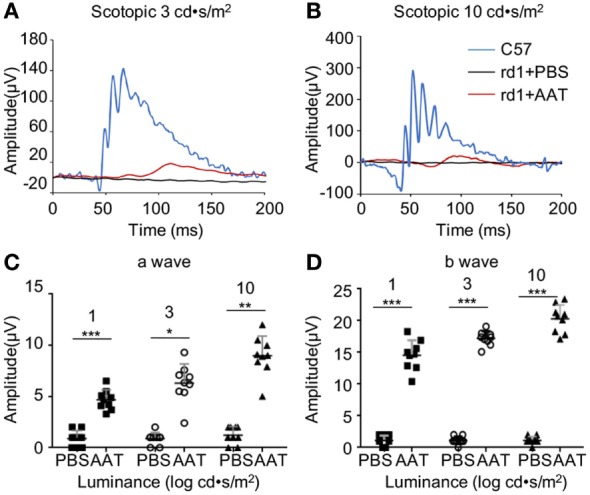
Alpha-1 antitrypsin (AAT) supplement protected retinal function in rd1 mice. (A,B) Retinal function was measured at P16 by electroretinogram using single-flash recordings at light intensities of 3.0 and 10.0 log cd•s/m2, respectively. C57 mice presented with typical a- and b-wave responses (n = 6), while the PBS-treated rd1 mice showed nearly undetectable amplitude of a- or b-waves under a variety of scotopic testing conditions. (C,D) AAT treatment induced mild increase in a-wave but significant elevation of b-wave amplitudes in the rd1 mice. n = 9 mice for each group. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two-tailed unpaired t-test).
