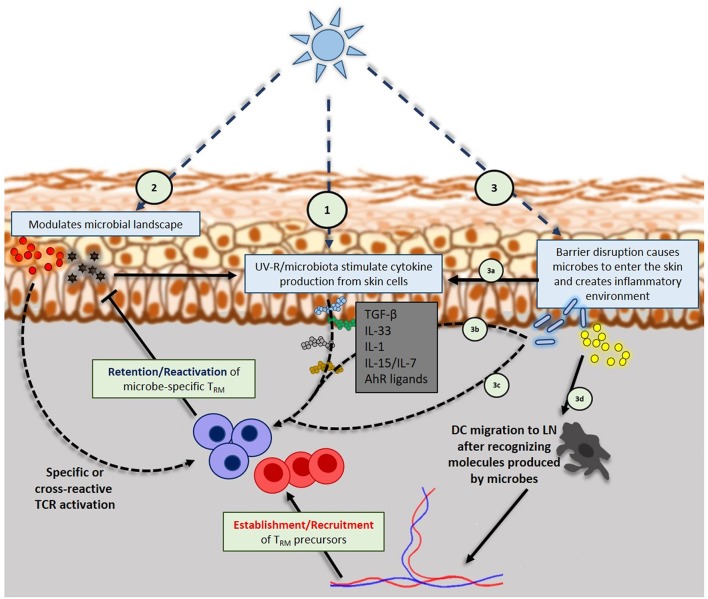
Figure 2.
Interplay of UV-R, skin microbiome and skin resident memory TCRαβ+ cells: (1) UV-R induces keratinocytes and other skin cells to produce inflammatory or regulatory cytokines that will influence TRM phenotype, retention and reactivation. (2) UV-R modulates microbial landscape, eventually releasing microbial antigens into the skin that will be up taken by dendritic cells (DC) that will specifically activate TRM (regulatory or effector). Microbial antigens can also trigger the production of inflammatory cytokines by keratinocytes that further activate TRM. (3) High doses of UV-R can cause barrier disruption that will allow skin resident microbes to enter the skin; danger signals from barrier disruption (3a) and microbes entered into the skin (3b) will trigger cytokines production by keratinocytes, DCs, ILCs, NK and TCRγδ cells. Those cytokines will take part in shaping TRM phenotype and activation. Entered microbes can also activate skin TRM in a specific manner (3c) or be uptaken by DCs (3d) in order to activate naïve specific T cells in draining lymph nodes that will be recruited on the site.