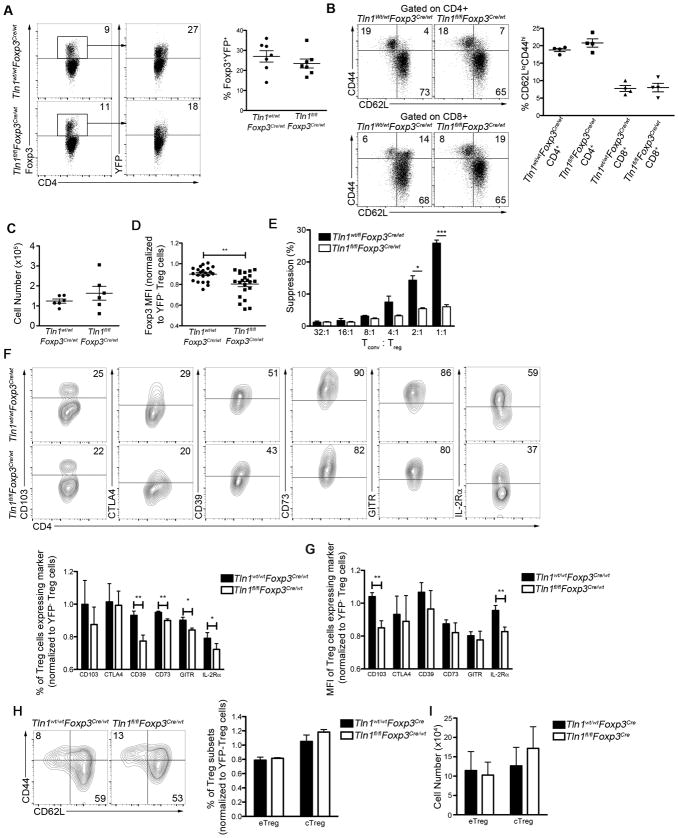
Figure 5. Talin controls the suppressive function of peripheral Treg cells.
(A) Percentages of talin-deficient Foxp3+ and YFP+ Treg cells from Tln1wt/flFoxp3Cre/wt or Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt mice, displayed cells gated on CD4+ events; n=7. (B) Percentages of splenic CD4+ (top) and CD8+ (bottom) T cells expressing CD44 and/or CD62L from female Tln1wt/wtFoxp3Cre/wt and Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt heterozygous mice; n=4. (C) Absolute number of Foxp3+YFP+ cells isolated from Tln1wt/wtFoxp3Cre/wt and Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt heterozygous mice; n=6. (D) Foxp3 MFI of Foxp3+YFP+ Treg cells from Tln1wt/wtFoxp3Cre/wt and Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt heterozygous mice, normalized to the Foxp3 MFI of Foxp3+YFP− wild-type Treg cells from each individual animal; n=22. (E) Suppression by sorted YFP+ Treg cells from Tln1wt/wtFoxp3Cre/wt or Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt mice at decreasing Tconv:Treg cell ratios, measured at 72 hours. Expression (F) and MFI (G) of putative suppressive molecules by splenic Treg cells from Tln1wt/wtFoxp3Cre/wt or Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt mice; displayed cells gated on CD4+Foxp3+YFP+ cells; n=5. (H and I) Percentage (H) and absolute number (I) of eTreg (CD62LloCD44hi) and cTreg (CD62LhiCD44lo) in Tln1fl/flFoxp3Cre/wt and control mice; n=5. Data are mean ± SEM and representative of at least 2 independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P <0.01, *** P <0.005, unpaired Student’s t-test.