Figure 7. MiR-155 expression in donor T cells is pivotal for donor T cell infiltration into target organs.
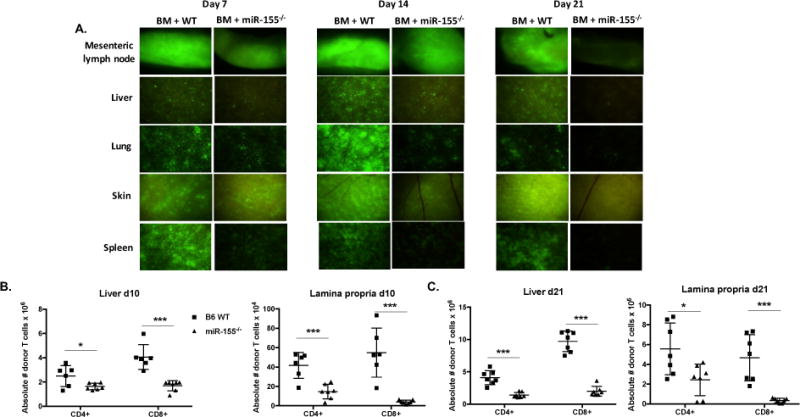
(A) BALB/c mice were lethally irradiated with 700cGy and transplanted with 10×106 B6 WT T cell depleted bone marrow cells and either 2×106 GFP+ B6 WT or GPF+ miR-155−/− CD25-depleted purified T cells. On days 7, 14, and 21, cohorts of mice were euthanized, and tissues taken for GFP (FITC) fluorescence stereomicroscopy. Zoom factors from 3.5× to 10× were used for imaging (3.5× for mesenteric lymph node; 7.0× for liver, spleen, and skin; and 10.0× for lung). N=3 mice per group per time point, with one representative tissue section shown. B6D2F1 mice were lethally irradiated with 1100cGy and transplanted with 10×106 B6 WT T cell depleted bone marrow cells and either 20×106 GFP+ B6 WT or GPF+ miR-155−/− splenocytes. On days 10 and 21, cohorts of mice were euthanized and both the whole liver and colon were harvested. N=6-7 mice in each group for each time point. Single cell suspensions were made of whole liver and colonic lamina propria and were then quantified by flow cytometry using CountBright Absolute Counting Beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific (B) Absolute numbers of donor CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the liver and colonic lamina propria day 10 post-transplant. (C) Absolute numbers of donor T cells in the liver and colonic lamina propria day 21 post-transplant. For all panels, NS p>0.05, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, and *** p<0.001.
