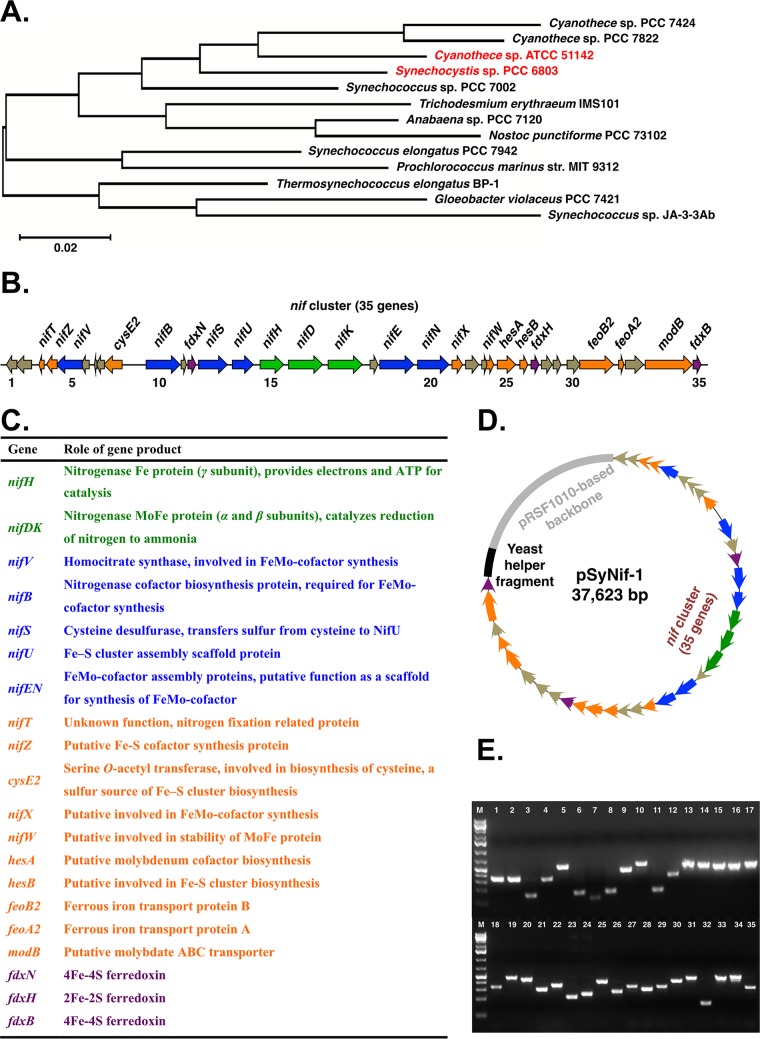
FIG 1 .
Introduction of nif genes into Synechocystis 6803. (A) Maximum likelihood 16S rRNA gene phylogeny of cyanobacteria. (B and C) Schemes showing the genetic organization of the nif cluster (B) and the role of each gene product (C) in Cyanothece 51142. Shown are the genes for the three structural proteins (nifHDK; green), necessary cofactors (blue), accessory proteins (orange), ferredoxins (purple), and hypothetical proteins (brown). Gene names and annotations are from GenBank (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/) and Cyanobase (http://genome.microbedb.jp/cyanobase). (D) A schematic map of plasmid pSyNif-1 containing the entire nif cluster. The backbone (gray) is from broad host plasmid pRSF1010, which can replicate in Synechocystis 6803. The yeast helper fragment (black) contains CEN6 and ARS as an ori and ura3 as a selection marker. (E) Transcription of all 35 genes in engineered Synechocystis 6803. Each lane represents a gene in the nif cluster, as numbered in panel B. Total RNA was extracted from cells cultured in BG110 medium under 12-h light/12-h dark conditions, and cDNA was used as the template for PCR.