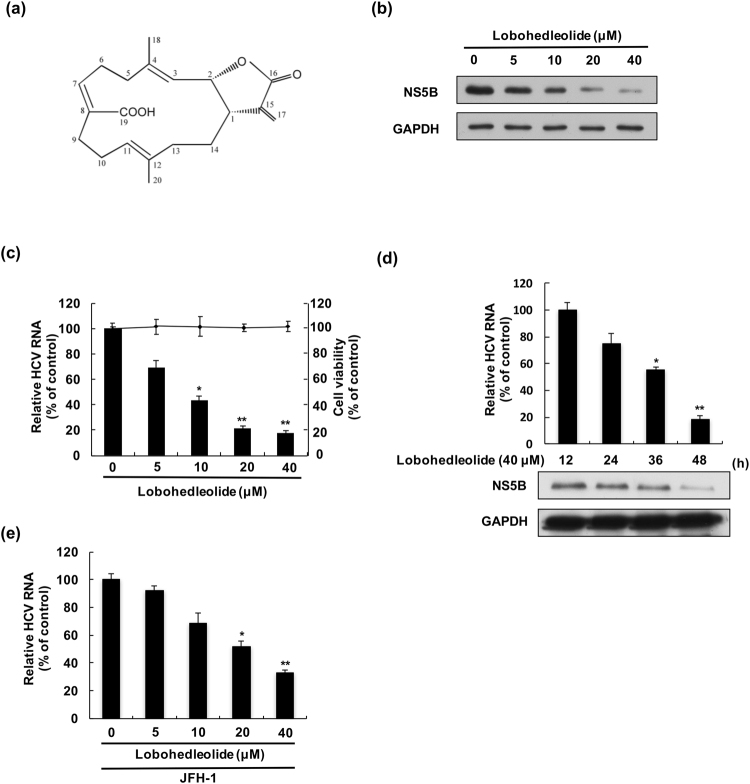
Figure 1.
The inhibitory effect of lobohedleolide on HCV replication. (a) The chemical structure of lobohedleolide. The reduction effect of lobohedleolide on HCV (b) protein synthesis and (c) RNA replication. Ava5 cells were treated with lobohedleolide at the indicated concentrations for 3 days. Cell viability was evaluated by MTS assay in the lobohedleolide-treated Ava5 cells. (d) Time-dependent inhibition of HCV protein synthesis and RNA replication by lobohedleolide. Ava5 cells were treated with 40 μM of lobohedleolide for the indicated time points. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with anti-HCV NS5B and anti-GAPDH antibodies. GAPDH served as an equal loading control in Western blotting. (e) Concentration-dependent inhibition of lobohedleolide in HCV JFH-1 infection system. Huh7.5 cells were infected with HCV JFH-1 at an MOI of 0.1 for 4 h, and the HCV-infected cells were treated with lobohedleolide at the indicated concentrations for another 3 days. Total cellular RNA was extracted, and the levels of HCV RNA were determined by qRT-PCR following the normalization of cellular gapdh mRNA level. The efficiency of inhibition was calculated as the percentage of control (0.1% DMSO treatment). Data are presented as mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments, with each measurement carried out in triplicate. Asterisks indicate significant difference in each sample of lobohedleolide-treated cells at the indicated concentration singly in comparison with DMSO-treated cells. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.