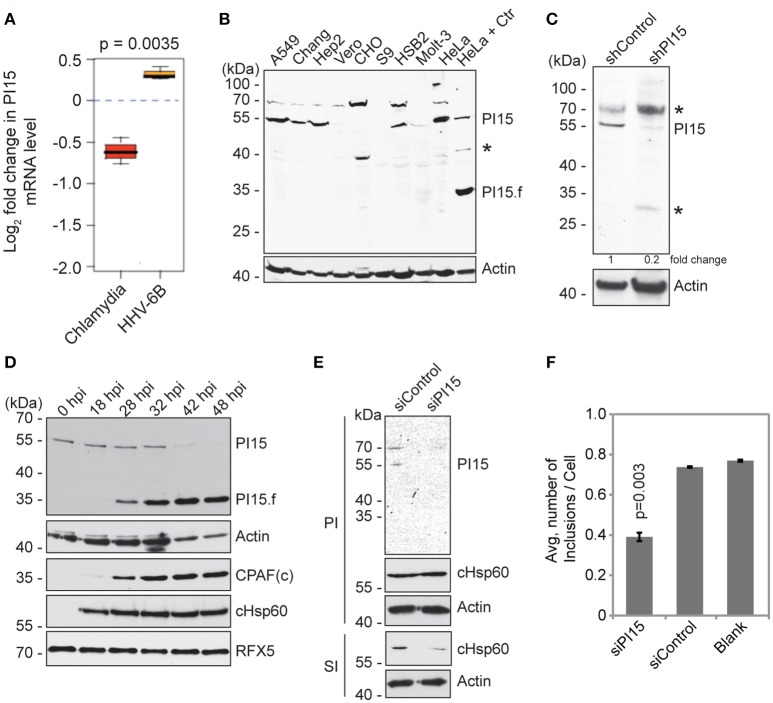
Figure 1.
PI15 expression is differentially regulated during Chlamydia infection. (A) PI15 is differentially regulated at the transcriptional level during Chlamydia and HHV-6B infection. HeLa cells were infected with C. trachomatis or HHV-6B for 24 h and PI15 RNA was detected by microarray analysis. (B) PI15 protein expression was analyzed in different cell lines by immunoblotting. Lysates from HeLa cells infected with C. trachomatis for 24 h were compared with the same from uninfected HeLa cells in the last two lanes. A549, human lung cells; Chang, human liver cells; Hep2, human epidermoid cancer cells; Vero, monkey kidney epithelial cells; CHO, Chinese hamster ovarian cells; S9, human bronchial epithelial cells; HSB-2 and Molt-3, human T-cell leukemia cells; HeLa, human cervical epithelial cells. Actin was used as a loading control. *, Unknown protein. (C) Identification of PI15 species that is silenced upon PI15-specific shRNA expression. HeLa cells were infected with either control lentiviral particles or with those that express shRNA against PI15. Protein lysates were verified for protein expression by immunoblotting. *, Unknown protein. (D) PI15 protein was cleaved during Chlamydia infection. HeLa cells were infected with C. trachomatis for different time intervals. Total lysates were prepared on ice using Laemmli sample buffer. Samples were processed for immunoblotting. CPAF and cHsp60 expression were tested as a control for chlamydial infection. Actin was used as a loading control and RFX5 expression was tested to monitor potential unwanted post lysis cleavage by CPAF. hpi, hours post infection; PI15.f, possible cleaved fragment of PI15; CPAFc, C-terminal fragment of activated CPAF. (E) siRNA-mediated silencing of PI15 inhibits chlamydial progeny formation. HeLa cells were transfected with siRNA against human PI15 for 72 h and were subsequently infected with C. trachomatis for another 36 h [Primary infection (PI)]. Parallel sets of experiments were carried out with cells transfected with scrambled siRNA controls. Secondary infection (SI) was carried out by applying lysed primary infected cells to fresh cells to test for Chlamydia growth and progeny formation under the influence of siRNAs. (F) Average number of chlamydial inclusions per cell was counted during secondary infection. Data represents ± SEM from 3 independent experiments.