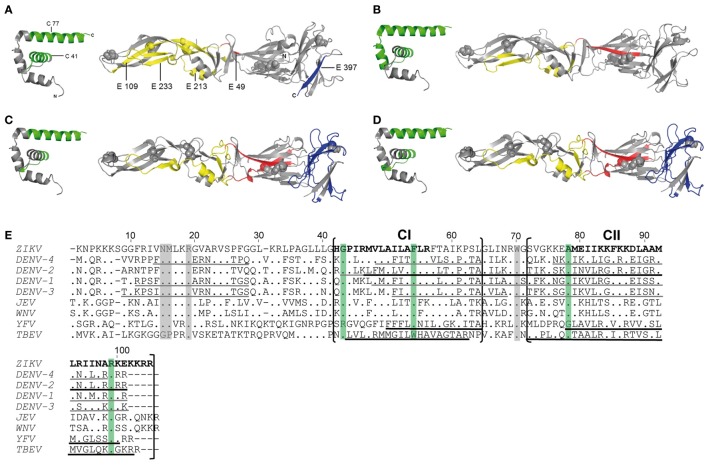
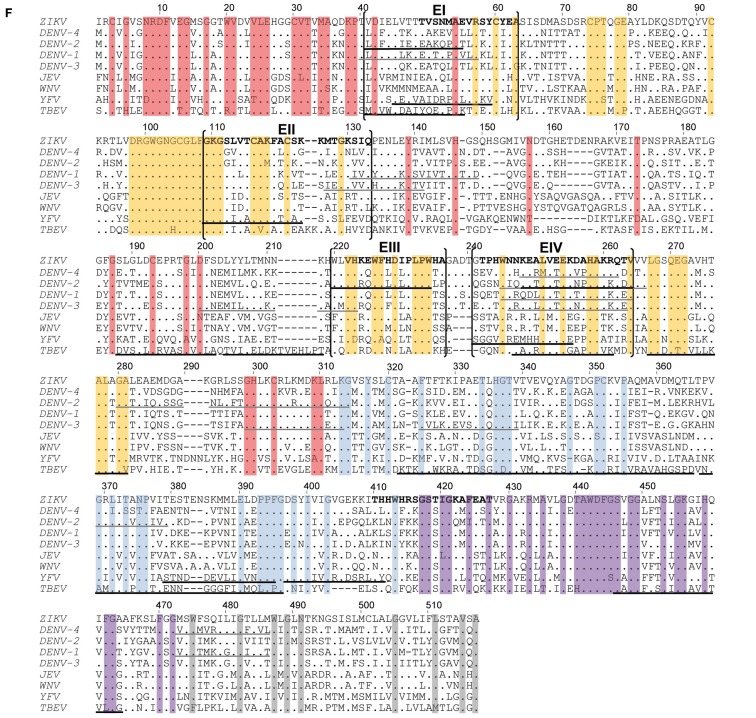
Figure 3.
Comparison of CD4 T cell epitope regions in C and E proteins of flaviviruses. [(A–D), left panel] Ribbon representation of the flavivirus Kunjin (KUN) C protein (PDB 1SFK). [(A–D), right panel] Ribbon representations of Zika virus (ZIKV) sE (PDB 5LBV) (13) (A), dengue (DEN)-2 virus sE (PDB 1OAN) (31) (B), tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) virus sE (PDB 1SVB) viruses (32) (C,D). Epitopes from Zika (A), DEN-2/4 (18, 19) (B), yellow fever (YF) (16) (C), and TBE (17) (D) viruses are colored as follows: C—green; E: domain I—red; domain II—yellow; domain III—blue. (E,F) Capsid (E) and envelope (F) protein sequence alignments of nine human-pathogenic flaviviruses. The C and E protein sequences from Zika (GenBank KJ776791), dengue (DEN) 1–4 (GenBank AF226687, M29095, DQ863638, GQ398256), Japanese encephalitis (JE) (GenBank D90194), West Nile (WN) (GenBank DQ211652), YF (GenBank CAA27332), and TBE (GenBank U27495) viruses were aligned using CLUSTAL omega. Experimentally determined epitopes from ZIKV are indicated in bold, those from DEN (18, 19), YF (16), and TBE (17) viruses are underlined in black and additional epitopes retrieved from the IEDB in gray. Sequence elements with ≥90% amino acid identity across all flaviviruses are highlighted as follows: C—green; E: domain I—red; domain II—yellow; domain III—blue; stem—purple; TM—gray.