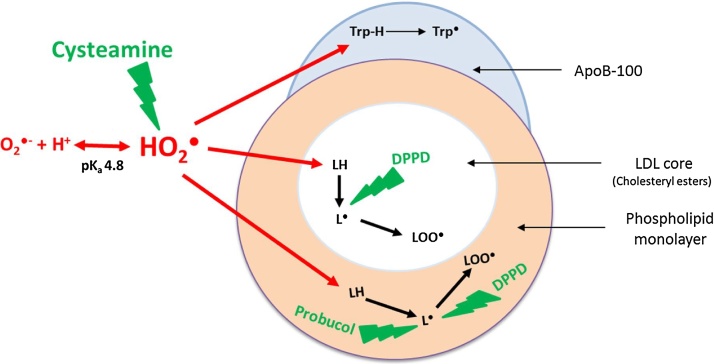
Fig. 8.
Oxidation of LDL by hydroperoxyl radicals at lysosomal pH. Iron in the lysosomes of macrophages leads to production of superoxide, which becomes protonated to the hydroperoxyl radical (HO2•), which attacks lipids (LH) in the both phospholipid monolayer and hydrophobic core of LDL and tryptophan residues in apoB-100. Probucol in the monolayer is unable to reach the hydrophobic core and thus cannot inhibit oxidation of cholesteryl esters, but does inhibit oxidation of the phospholipid monolayer. DPPD is more hydrophobic than probucol and inhibits oxidation in both the monolayer and core. Cysteamine scavenges hydroperoxyl or superoxide radicals in the aqueous phase and is able to inhibit the oxidation of LDL in both the core and monolayer.