Fig. 13.1.
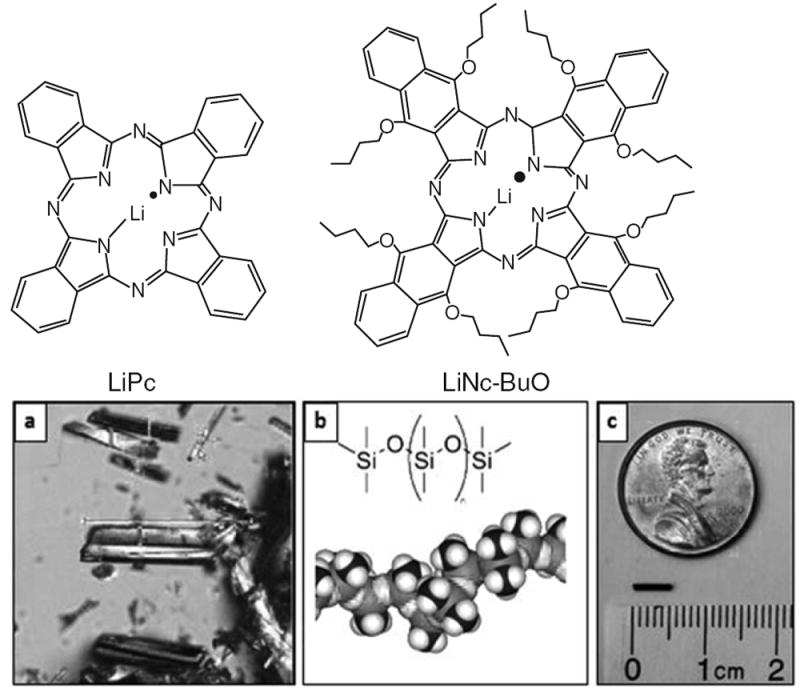
(a) Molecular structure of lithium phthalocyanine (LiPc) and lithium octa-n-butoxynaphthalocyanine (LiNc-BuO) oximetry probes. The probes are prepared in the form of fine crystals which are paramagnetic and biologically inert. The crystals exhibit high spin density (~1020 spins/g), single sharp EPR peak (peak-to-peak width <50 mG under anoxic conditions), and are sensitive to oxygen partial pressure of oxygen (5–9 mG/mmHg pO2). (b) LiNc-BuO crystals, PDMS coating, and the OxyChip. (A) Microcrystals of LiNc-BuO are encapsulated into (B) polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), a biocompatible and oxygen-permeable polymer, to obtain (C) small pieces of probes (OxyChip) for implantation in tissues. The OxyChip is 0.6 mm in diameter and 5 mm in length and can be conveniently loaded into the tip of an 18-G angio-catheter to be implanted in tumors. (b [B] is reproduced from Courtney 2015 [23])
