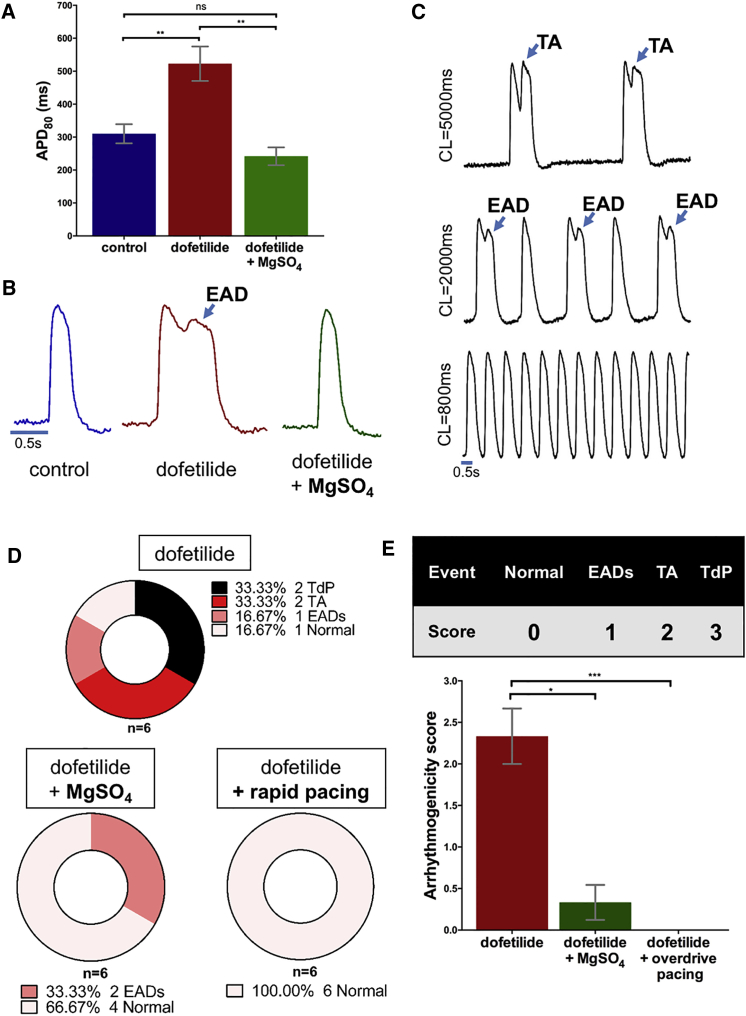
Figure 7.
Prevention of Dofetilide-Induced Arrhythmogenicity by Rapid Pacing and Magnesium Sulfate
(A) Summary of dofetilide and dofetilide + MgSO4 supplementation effects on APD80 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc analysis, n = 6 from three independent experiments for each group).
(B) Representative optical APs from ArcLight-hiPSC-CCS after treatment with dofetilide or dofetilide + MgSO4.
(C) Optical APs from ArcLight-hiPSC-CCS showing arrhythmogenic activity (TA and EAD) at slow pacing frequencies (CL, 5,000 and 2,000 ms) and their suppression at higher pacing frequency (CL, 800 ms).
(D) Summary of dofetilide-induced arrhythmogenicity in ArcLight-hiPSC-CCSs and its suppression by MgSO4 supplementation and rapid pacing.
(E) Arrhythmogenicity scoring system and summary of MgSO4 supplementation and rapid pacing on ArcLight-hiPSC-CCSs' arrhythmogenicity score (Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparison, n = 6 from three independent experiments for each group).
Values are presented as means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Video S6. Dofetilide-Induced Arrhythmogenesis #1, Related to Figures 6 and 7 and Videos S7 and S8, Video S7. Dofetilide-Induced Non-propagating EADs, Related to Figures 6 and 7 and Videos S6, S8, and S9, Video S8. Dofetilide-Induced Propagating TA, Related to Figures 6 and 7 and Videos S6, S7, and S9, Video S9. Dofetilide-Induced Arrhythmogenesis #2, Related to Figures 6 and 7 and Videos S6–S8.