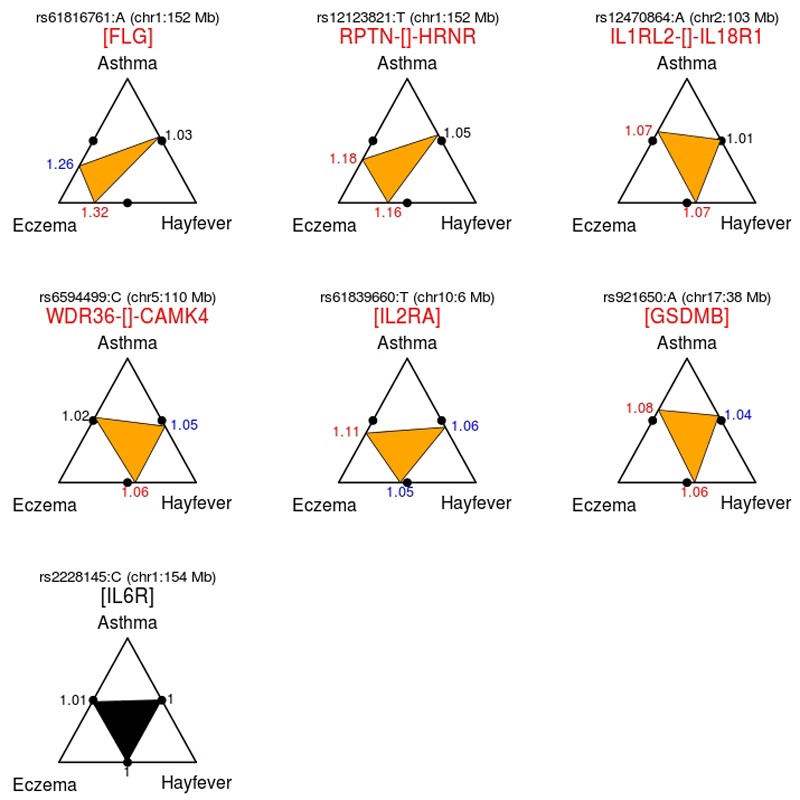
Figure 2. Sentinel variants with significant allele-frequency differences in pairwise case-only association analyses contrasting individuals suffering from a single allergic disease.
For each sentinel variant, we performed three case-only association analyses, comparing asthma-only cases (n=12,268) against hay fever-only cases (n=33,305); asthma-only cases against eczema-only cases (n=6,276); and hay fever-only cases against eczema-only cases. After accounting for multiple testing, significant associations for at least one of these analyses were only observed for six of the 136 sentinel variants, which are shown in the first two rows of the figure. For a given variant, the vertices of the inner triangle point to the position along the edges of the outer triangle that corresponds to the allele frequency difference observed between pairs of single-disease cases. For example, the rs61816761:A allele, which is located in the Fillagrin gene (FLG), was 1.32-fold more common in individuals suffering only from eczema when compared to individuals suffering only from hay fever (P=7.2x10-8), consistent with this SNP being a stronger risk factor for eczema than for hay fever. A similar result (OR = 1.26, P=0.0004) was observed for this variant when contrasting eczema-only cases against asthma-only cases. For comparison, a variant with no allele frequency differences in all three pairwise single-disease association analyses is also shown (rs2228145, in the IL6R gene). In this case, the three estimated odds ratios were approximately equal to 1. The color of the OR font reflects the significance of the association: red for P<1.2x10-4 (correction for multiple testing), blue for P<0.05 and black for P>0.05.