Figure 1. Illustration of integrative modeling.
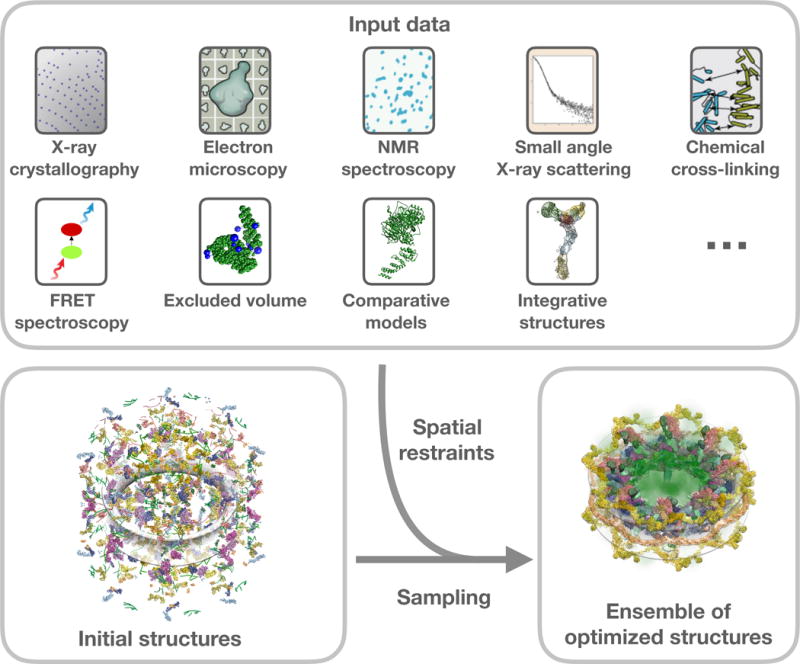
Examples of experimental and computational methods that can provide spatial restraints for integrative modeling (top). Atomistic and coarse-grained starting structural models of components of a macromolecular assembly are shown in various representations (bottom left). Extensive conformational and/or configurational sampling is carried out to yield the optimized assembly models that satisfy the input spatial restraints (bottom right).
