Fig. 2.
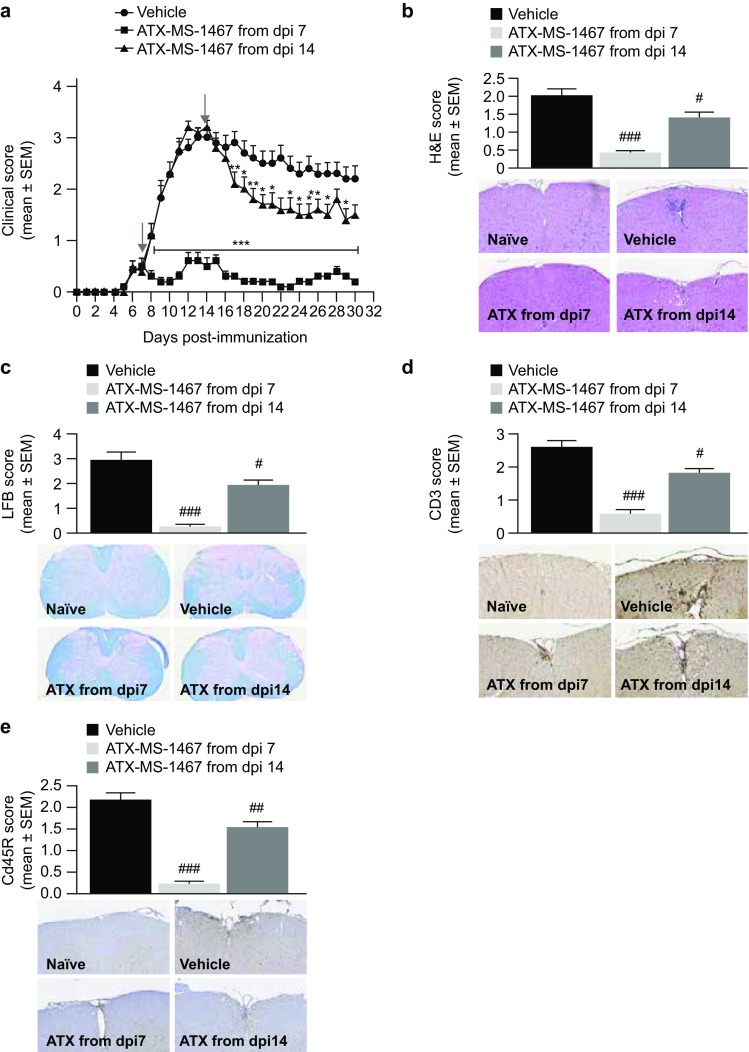
Effect of therapeutic treatment with ATX-MS-1467 on spinal cord tissue damage in spinal cord homogenate-induced EAE in (DR2 × Ob1)F1 mice. a The effect of 100-µg ATX-MS-1467 treatment starting at 7 or 14 dpi on daily clinical scores and on terminal (day 30) histological scores. The arrows indicate the beginning of the treatment period in each group. *, ** and *** indicate p < 0.05, < 0.01 and < 0.001, respectively, by Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s test versus vehicle. H&E staining was applied to assess inflammation (b), luxol fast blue staining was applied to assess demyelination (c), and immunohistochemical staining for CD3 or CD45R was applied to assess T-cell (d) and B-cell infiltration (e). The inserts show representative images for each group with the respective staining for which the semi-quantitative evaluation is plotted. #, ## and ### indicate p < 0.05, < 0.01 and < 0.001, respectively, by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni versus mice treated with vehicle (PBS). The data represent a pool from 2 independent experiments with a total of 20–28 mice. Spinal cords from naïve mice were also processed, stained and analyzed along with the samples from the immunized/treated mice. The histological (as well as clinical) scores for naïve mice was zero for all cases; therefore, for the sake of simplicity, data from naïve mice was not included in the graphs. dpi days post-induction, EAE experimental autoimmune encephalitis, H&E hematoxylin & eosin, LFB luxol fast blue, PBS phosphate-buffered saline, SEM standard error of the mean
