Fig. 5.
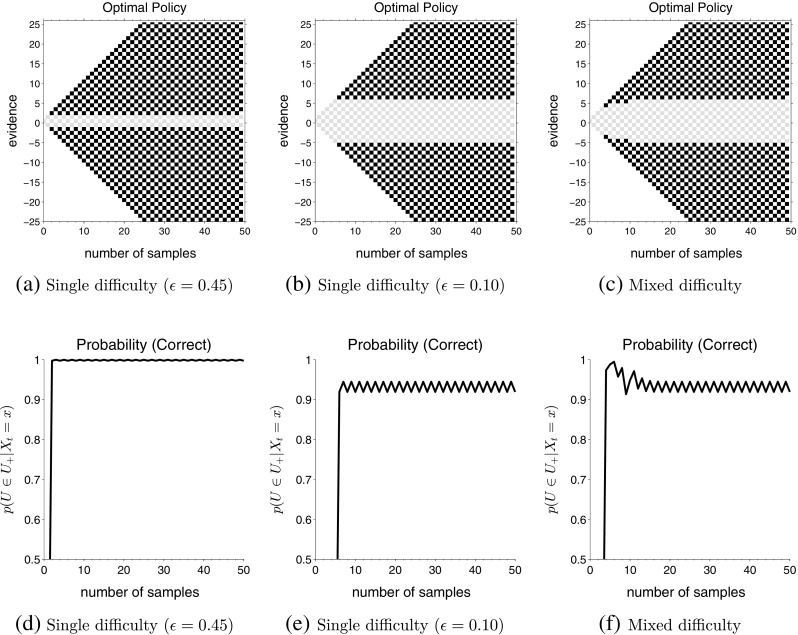
Optimal actions for a mixture of difficulties when the easy task has narrower bounds than the difficult task. The inter-trial delays for all three computations are D C = D I = 150. Panels (a) and (b) show optimal policies for single difficulty tasks with up-probability of each decision chosen from u ∈{0.05,0.95} and u ∈{0.40,0.60}, respectively. Panel (c) shows optimal policy in mixed difficulty task with up-probability chosen from u ∈{0.05,0.40,0.60,0.95} and . Panels (d–f) show the change in posterior probabilities with time at the upper decision boundary for conditions (a–c), respectively
