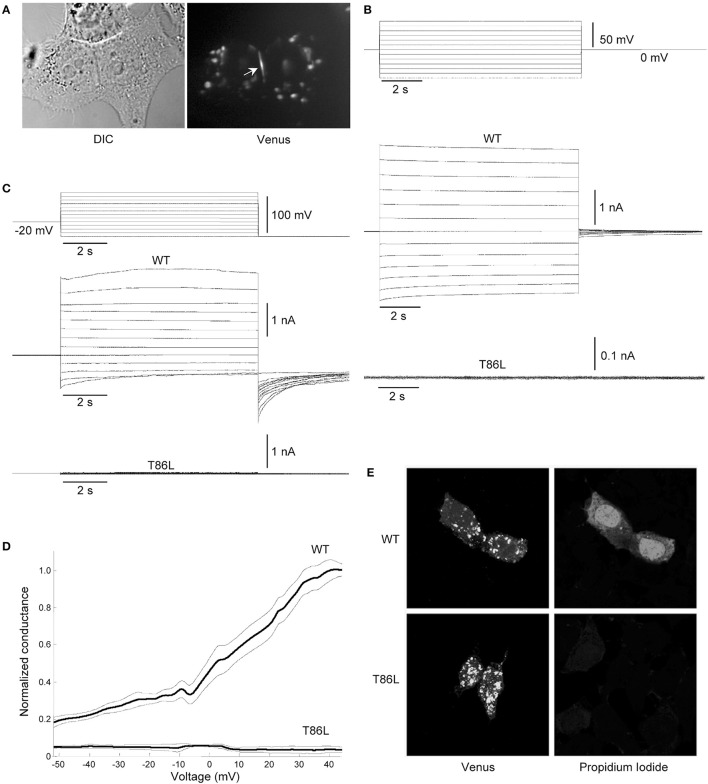
Figure 8.
Patch clamp and dye-uptake assays in HeLa DH transfectants. (A) Left: differential contrast image (DIC) of HeLa DH cells transiently transfected with hCx26T86L fused in frame with the GFP color mutant Venus; right: same field of view under fluorescence illumination, highlighting a gap junction plaque between a pair of adjacent cells (arrow). Cytosolic fluorescent puncta are consistent with previous analysis of connexin trafficking en route to the plasma membrane (Thomas et al., 2005). (B) Voltage commands applied to cell 1 (top traces) elicited junctional currents in the adjacent cell (cell 2) of a pair of HeLa DH cells transiently trasfected with wild type (WT) hCx26 (middle traces); junctional currents were undetectable in T86L transfectants (bottom traces). (C) Representative measurements of hemichannel currents elicited by voltage commands (top traces) in HeLa DH cells transiently trasfected with wild type (WT) hCx26 (middle traces); hemichannel currents were undetectable in T86L transfectants (bottom traces). (D) Membrane conductance in response to slow (400 s) voltage ramps from nominal +60 to −60 mV; ordinates were normalized by the mean conductance of WT hCx26 at +40 mV; abscissas were corrected for the voltage drop due to the access resistance (18 ± 3 MOhm for T86L, n = 6; 19 ± 5 MOhm for WT, n = 6); measurements in (B,C) were performed in 0.2 mM extracellular Ca2+. (E) Incubating HeLa DH cells for 60 min in nominally Ca2+-free extracellular solution containing Propidium Iodide 0.25 mM promoted dye uptake in cells expressing WT hCx26 (top), whereas cells expressing the T86L mutant failed to uptake the dye (bottom).