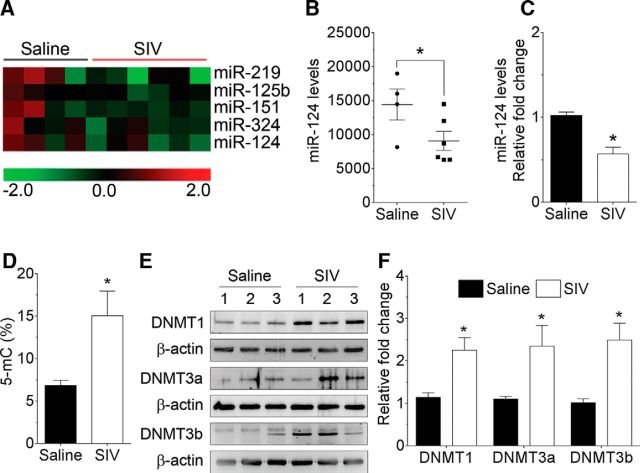
Figure 1.
SIV infection downregulates miR-124 and increases the DNMTs levels in the basal ganglia of rhesus macaques. A, Unbiased heatmap of the expression profiles of miRNAs in the basal ganglia of saline (n = 4) and SIV-infected rhesus macaques (n = 6) (both sexes). B, Mean fluorescent intensity of miR-124, as measured by miR microarray, in the basal ganglia of saline (n = 4) and SIV-infected rhesus macaques (n = 6). C, qPCR analysis showing the significant downregulation of miR-124 expression in the basal ganglia of SIV-infected rhesus macaques compared with the saline group. D, Quantification of 5-mC using ELISA showing the increased levels of 5-mC in the basal ganglia of SIV-infected rhesus macaques compared with the saline group. E, F, Representative Western blots showing the increased levels of DNMT1, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b in the basal ganglia of SIV-infected rhesus macaques compared with the saline group. β-Actin was probed as a protein loading control for all the experiments. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 versus saline (unpaired Student's t test).