Figure 3.
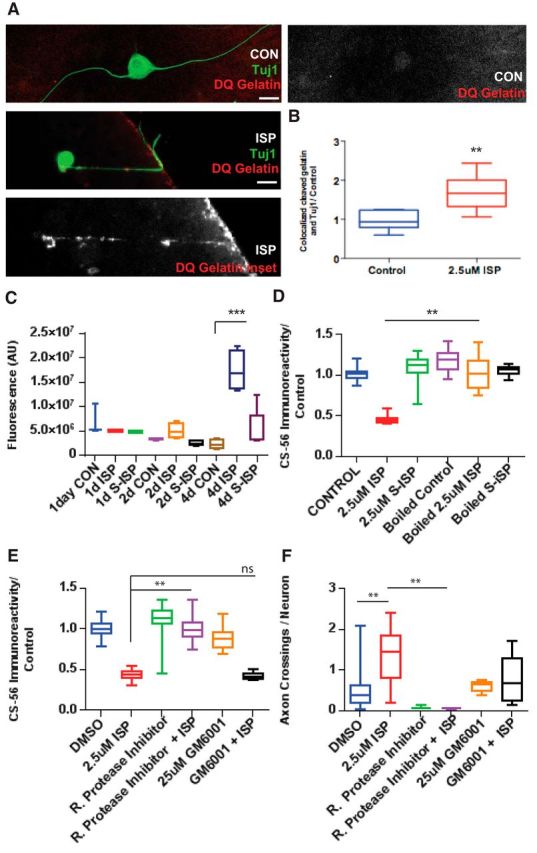
ISP promotes GAG chain degradation through increasing protease activity. A, Representative image of an ISP-treated DRG axon digesting DQ Gelatin as it crosses the CSPG gradient in our spot assay and vehicle control DRG axon. Scale bar, 50 μm. B, Quantification of ratio of cleaved DQ Gelatin overlapping Tuj1-labeled axons (n = 34, 32; t = 4.025, df = 15, p = 0.0011, unpaired t test). C, EnzChek measures fluorescence of cleaved casein of CM from DRGs treated with CON, 2.5 μm ISP or SISP for 1, 2, or 4 DIV (n = 11, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 19, 18, 20; F(8,27) = 15.4, p = 0.0001; ANOVA). D, Aggrecan spot GAG chain degradation is rescued following boiling CM, then incubating with guanidine hydrochloride (5 m) before plating (n = 71, 49, 50, 51, 68, 50; F(5,87) = 37.13, p = 0.0001; ANOVA). E, Aggrecan spot degradation was rescued by 0.1% Roche general protease inhibitor mixture, but not broad MMP inhibitor, GM6001 (25 μm) (n = 114, 161, 197, 97, 100, 63; F(5,112) = 82.05, ISP vs RPI+ISP, p = 0.001; ISP vs GM6001+ISP, not significant, p = 0.9964; ANOVA). F, Axon crossings, normalized by the total number of neurons in the spot, were decreased with protease inhibitor treatment (n = 28, 10, 10, 29, 17, 20; F(5,37) = 5.255, DMSO vs ISP, p = 0.0042; ISP vs RPI+ISP, p = 0.0064; ANOVA). Lines indicate median. Boxes represent quartiles. Whiskers indicate range. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
