Fig. 6.
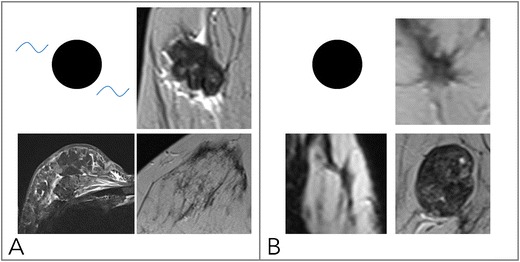
Diagnostic criteria: oedema. As shown in (A), oedema is present if fluid-caused T2w hyperintensity not attributable to cysts or dilated ducts is identified in the breast that harbours an enhancing lesion. Odema may be perifocal [A, upper right (mass) and lower right (non-mass)] or more diffuse (A, lower left, showing subcutaneous, diffuse, and pre-/intrapectoral oedema in an inflammatory breast cancer case with distinct lymphangiosis). B: Absent oedema. The common pitfall causing false-positive oedema assessment is chemical shift artefacts in sharp fat-water interfaces, such as that caused by vessels (e.g., B upper right, lower right) and capsulated fibroadenomas at the parenchyma-fat interface
