Fig. 2.
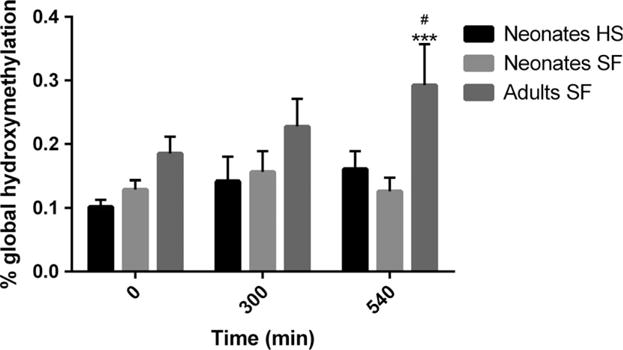
Effects of post-mortem interval and tissue heat stabilization (HS) on global 5hmC levels in cerebellum. To study the effect of post-mortem interval, the cerebellum from three groups of neonatal and adult animals were kept at room temperature for 0–540 min. before they were snap-frozen (SF) and stored at −80°C. To determine the effect of HS, the cerebellum from three groups of neonatal animals were instantly heat-stabilized and kept at room temperature for 0–540 min. before storage. Values represent mean ± S.E.M. ***p < 0.001, compared with the neonate SF group at respective time-points. #p < 0.05 compared with the adult 0-min. group. No differences were demonstrated between the neonatal SF and HS groups (ANOVA followed by Fisher’s LSD test).
