FIGURE 2.
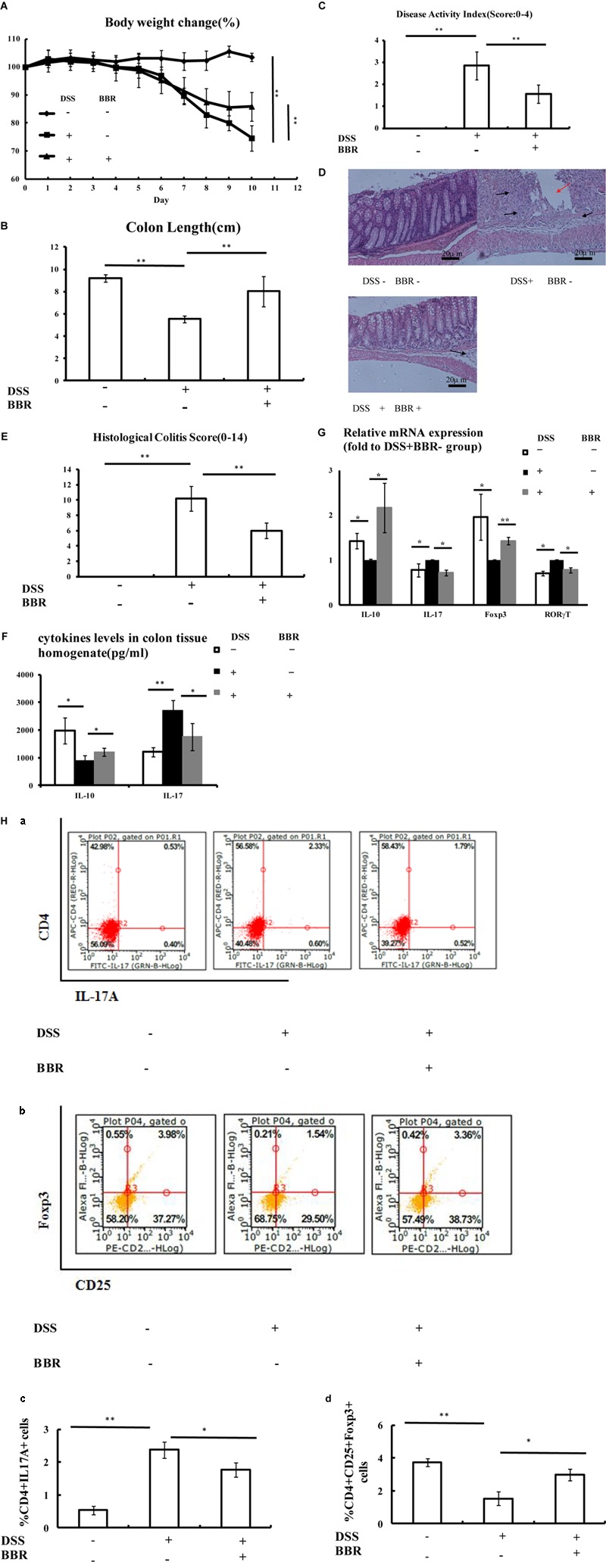
Berberine (BBR) improved Treg/Thl7 balance in DSS-induced UC model mice. (A,B) Body weight loss and shorten of colon length were reduced after BBR treatment in DSS-induced UC model mice; (C) Mice treated with BBR had a lower DAI score compared with DSS treated mice; (D,E) H&E staining (Arrows in red indicate mucosal necrosis, arrows in black indicate inflammatory cell infiltration; 20x) and histological colitis score showed that BBR reduced mucosal necrosis and inflammatory cell infiltration in colon; (F) BBR treatment increased IL-10 and decreased IL-17 levels of colon tissue homogenate in DSS-induced UC model mice; (G) After BBR treatment, the relative mRNA expression of IL-10 and Foxp3 in colonic mucosa was upregulated whereas the relative mRNA expression of IL-17 and RORγT in colonic mucosa was downregulated as compared with DSS+BBR– group (Fold to DSS+BBR– group); (H) Flow cytometric analysis showed that BBR treatment decreased the numbers of CD4+IL17A+ (a: plot; c: graph) cells and increased the numbers of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ (b: plot; d: graph) in spleen compared with DSS+BBR– group. DSS–BBR–; DSS+BBR–; DSS+BBR+ (n = 10 per group, for A–G). DSS–BBR–; DSS+BBR–; DSS+BBR+ (n = 6 per group, H). Data are presented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
