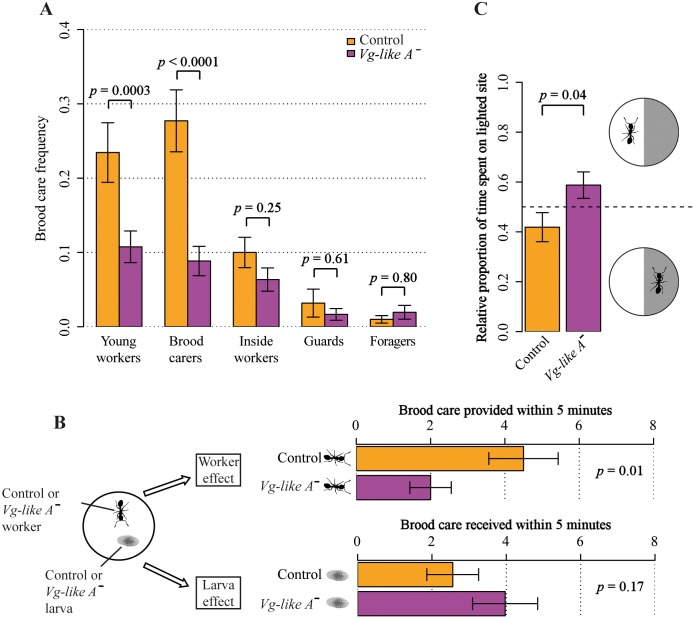
Fig 3. Short-term knockdown of Vg-like A reduced brood care behavior.
(A) Brood care frequency was influenced by an interaction between treatment (control, Vg-like A−) and caste (GLMM: p < 0.0001). A down-regulation of Vg-like A decreased brood care behavior in young workers and brood carers but not in other castes. (B) Workers and larvae were tested (n = 65) in a full-factorial design regarding worker and larval treatment (control, Vg-like A−) in individualized tests. Brood care conducted by workers was counted for 5 minutes every 15 seconds. Vg-like A knockdown–associated decrease in brood care can be explained by worker treatment but not by larval treatment. (C) Vg-like A− brood carers exhibited lower light aversion. Brood carers of both treatments were individually transferred to half-darkened petri dishes. For 60 minutes, position (darkened or lighted site of the dish) was recorded every 5 minutes. Dashed line at 50%, i.e., same time spent on each site. GLMM, generalized linear mixed model; Vg, vitellogenin.