Fig. 5.
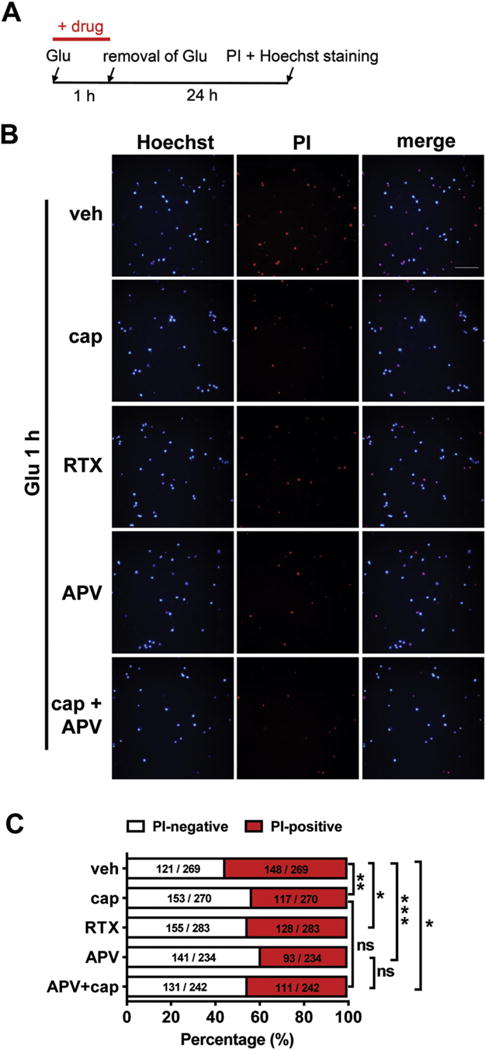
Capsaicin treatment attenuates glutamate-induced neuronal death in cultured mouse cortical neurons. (A) Timeline of the drug treatment and propidium iodide (PI)/Hoechst staining. (B) and (C) Attenuation of glutamate-induced neuronal death by capsaicin (cap, 3 pM), a potent TRPV1 agonist RTX (10 nM), NMDA antagonist APV (50 μM), or APV combined with capsaicin treatment in cultured cortical neurons. ns, no statistical significance. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test of one representative group. At least three parallel experiments were repeated. (B) Representative images show the protective effects of capsaicin, RTX, APV or combined treatment of APV and capsaicin on glutamate-induced neuronal death. Scale bar = 50 pm. (C) Quantification of the glutamate-induced neuronal death with the different drug treatment as shown in (B).
