Fig. 8.
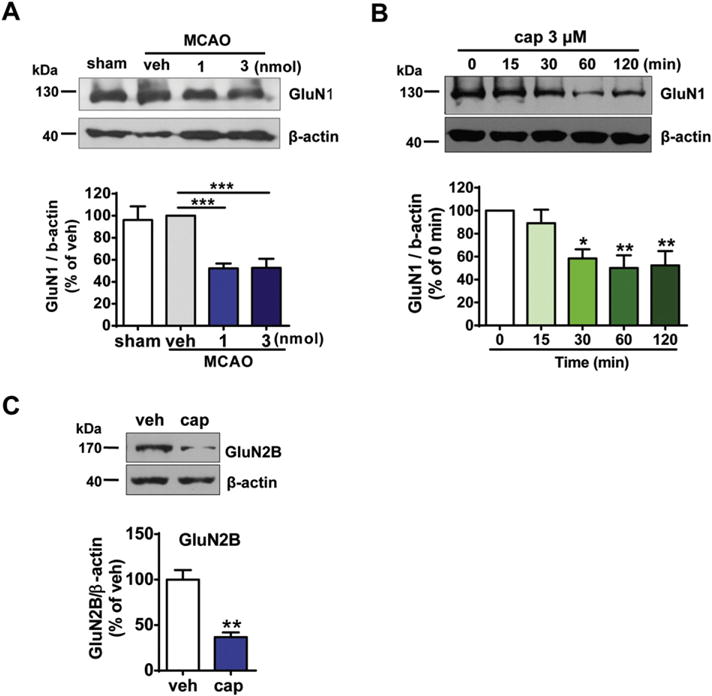
Capsaicin treatment down-regulates the amount of NMDA receptors. (A) The amount of GluN1 subunit was significantly reduced after capsaicin injection into the peri-infarct area of MCAO/reperfusion rats. Peri-infarct tissue was collected 1 h after reperfusion following 2 h MCAO. Capsaicin was injected 0.5 h after reperfusion. n = 3–4, ***p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc tests. (B) Time-dependent decrease in the GluN1 protein after capsaicin (cap, 3 μM) treatment in the rat cortical neurons. n = 5, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc tests. (C) The expression of GluN2B subunit of NMDA receptors was decreased after capsaicin (3 μM) treatment for 1 h in rat cortical neurons. n = 6, **p < 0.01, paired t-test
