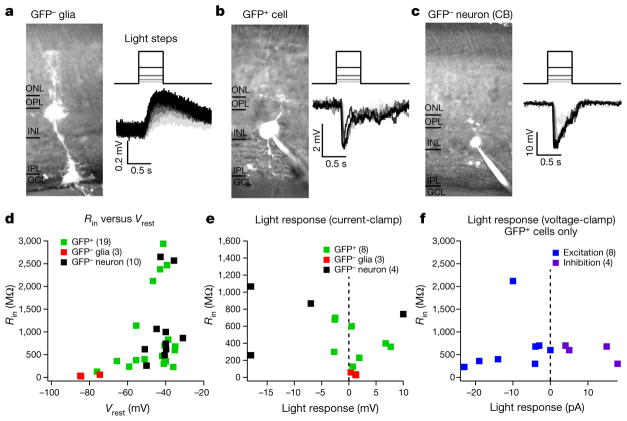
Figure 3. MG-derived GFP+ cells exhibit larger and faster visual responses than normal GFP− MG.
a–c, Example recordings from GFP− MG (a), MG-derived GFP+ cell (b) and GFP− cone bipolar cell (c). Traces are visual responses to 500-ms steps in luminance, recorded in current-clamp. d, Population data for input resistance and resting membrane potential measurements. e, Population data for visual responses recorded with the current-clamp technique. f, Population data for light-evoked excitatory and inhibitory synaptic inputs recorded with the voltage-clamp technique. All cells recorded were from five ANT-treated mice. Recordings were performed at 4, 5, 10, 12 and 15 weeks post-TSA. Visual responses were found in cells regardless of post-TSA duration. GFP− MG: Vrest, −81 ± 6 mV; Rin,41 ±17 MΩ; maximal response to light stimulation, 0.95 ± 0.52 mV; n = 3. GFP+ cells: Vrest, −46±11 mV, n = 19; Rin, 871 ±868 MΩ, n = 20; maximal response to light stimulation, 3.2 ±2.7 mV, n = 8; excitatory input, −10±8 pA, n = 8; inhibitory input, 10 ±7 pA, n = 4. GFP− neurons: Vrest, −42±6 mV, n = 10; Rin, 1,088 ±836 MΩ, n = 10; maximal response to light stimulation, 13 ±6 mV, n = 4. All responses are written mean ±s.d.