Figure 3. Immune checkpoint protein expression in HIV and HBV infection and potential effects of immune checkpoint blockade.
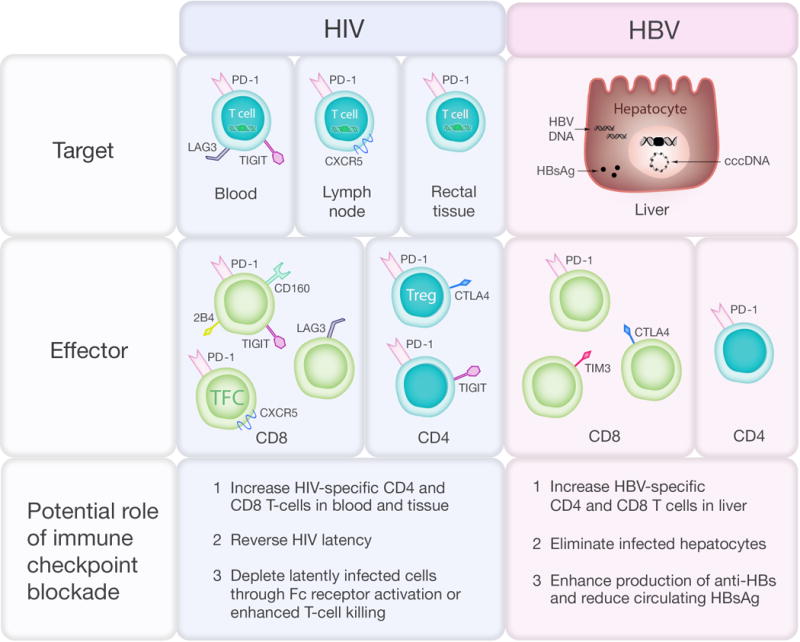
In HIV infection, the virus persists on antiretroviral therapy (ART) in latently infected CD4+ T-cells that contain integrated provirus (green box) and express PD-1 and other immune checkpoint markers in blood, lymph node and rectal tissue. Expression of immune checkpoint markers on total and HIV-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cell subsets include central memory (CM), effector memory (EM), T follicular cytotoxic (TFC) and T regulatory (Treg) T cells is associated with T-cell exhaustion and reduced T-cell function. In HBV infection, HBV persists on treatment as extrachromosomal closed covalent circular (ccc) DNA and integrated HBV DNA (black box) and there is ongoing production of HBV surface antigen (HBsAg). Increased expression of immune checkpoint markers on CD8+ T cells and increased expression of PD-1 on CD4+ T-cells reduce T cell function.
