Figure 1. Increased IgA-producing blood plasmablasts in IPAH.
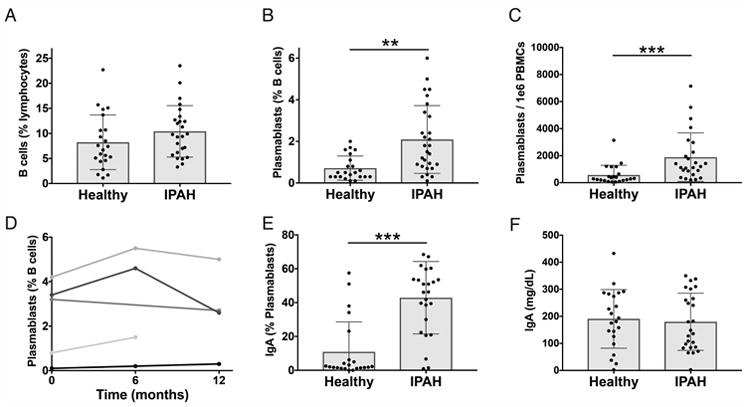
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and plasma were isolated from the blood of IPAH and healthy individuals. (A-C) Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry for CD19+ B cells (A), CD19+/INTCD3-CD14-CD20-CD27+CD38hi plasmablasts as a percent of CD19+ cells (B), and plasmablasts per 1×106 PBMCs (C). Each bar represents the mean ± SD of all subjects in a group and each dot represents the measured value for one subject with n = 25 (IPAH), n = 22 (Healthy).(D) Stability of plasmablast numbers over time in five individual IPAH patients for whom serial samples were available. Each line represents an individual subject. (E) Proportion of circulating plasmablasts with surface IgA expression. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of all subjects in a group and each dot represents the measured value for one subject with n = 25 (IPAH), n = 22 (Healthy). (F) Total serum IgA, measured by ELISA. Each bar represents the mean ± SD of all subjects in a group, and each dot represents the mean value of two replicate wells from an individual subject with n = 25 (IPAH), n = 22 (Healthy). IgA ELISA data was collected in a single independent experiment, while flow cytometry measurements were performed in batches of 1 to 5 patients, together with controls, at the time of the patient's medical visit. Cumulative data from all batches of flow cytometry is shown. ***P<0.001, **P<0.01 by Student's t-test.
